Use of atorvastatin as an anti-inflammatory treatment in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 18806816
- PMCID: PMC2597264
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.369
Use of atorvastatin as an anti-inflammatory treatment in Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: Experimental and clinical investigations have revealed that statins can downregulate both acute and chronic inflammatory processes. Whether statins express anti-inflammatory activities in the treatment of Crohn's disease is unknown.
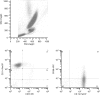
Experimental approach: Ten patients were given 80 mg atorvastatin once daily for 13 weeks and then followed up for 8 weeks after the treatment. The anti-inflammatory effects of statin were assessed by measuring levels of plasma C-reactive protein (CRP), soluble (s) CD14, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, sTNFRI and II, CCL2 and 8 and the mucosal inflammation by faecal calprotectin. Circulating monocytes were subgrouped and their chemokine receptor expression of CCR2 and CX(3)CR1 were analysed.
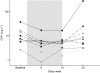
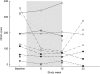
Key results: In 8 of 10 patients, atorvastatin treatment reduced CRP (P=0.008) and sTNFRII (P=0.064). A slight decrease in plasma levels of sCD14, TNF-alpha and sTNFRI was observed in 7/10 patients and faecal calprotectin was reduced in 8/10 patients. We also observed that the treatment diminished expression of CCR2 and CX(3)CR1 on monocyte populations (P=0.014). At the follow-up visit, 8 weeks after the atorvastatin treatment was terminated, CRP levels had returned to those seen before the treatment.
Conclusions and implications: Our findings imply that atorvastatin therapy reduces inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease and, therefore, encourage further investigations of statin-mediated protective effects in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Arias MA, Rey Nores JE, Vita N, Stelter F, Borysiewicz LK, Ferrara P, et al. Cutting edge: human B cell function is regulated by interaction with soluble CD14: opposite effects on IgG1 and IgE production. J Immunol. 2000;164:3480–3486. - PubMed
-
- Banks C, Bateman A, Payne R, Johnson P, Sheron N. Chemokine expression in IBD. Mucosal chemokine expression is unselectively increased in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. J Pathol. 2003;199:28–35. - PubMed
-
- Bas S, Gauthier BR, Spenato U, Stingelin S, Gabay C. CD14 is an acute-phase protein. J Immunol. 2004;172:4470–4479. - PubMed
-
- Berstad A, Arslan G, Folvik G. Relationship between intestinal permeability and calprotectin concentration in gut lavage fluid. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000;35:64–69. - PubMed
-
- Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976;70:439–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

