Nanobiosensors: optofluidic, electrical and mechanical approaches to biomolecular detection at the nanoscale
- PMID: 18806888
- PMCID: PMC2544611
- DOI: 10.1007/s10404-007-0198-8
Nanobiosensors: optofluidic, electrical and mechanical approaches to biomolecular detection at the nanoscale
Abstract
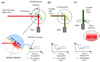
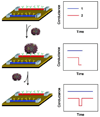
Next generation biosensor platforms will require significant improvements in sensitivity, specificity and parallelity in order to meet the future needs of a variety of fields ranging from in vitro medical diagnostics, pharmaceutical discovery and pathogen detection. Nano-biosensors, which exploit some fundamental nanoscopic effect in order to detect a specific biomolecular interaction, have now been developed to a point where it is possible to determine in what cases their inherent advantages over traditional techniques (such as nucleic acid microarrays) more than offset the added complexity and cost involved constructing and assembling the devices. In this paper we will review the state of the art in nanoscale biosensor technologies, focusing primarily on optofluidic type devices but also covering those which exploit fundamental mechanical and electrical transduction mechanisms. A detailed overview of next generation requirements is presented yielding a series of metrics (namely limit of detection, multiplexibility, measurement limitations, and ease of fabrication/assembly) against which the various technologies are evaluated. Concluding remarks regarding the likely technological impact of some of the promising technologies are also provided.
Figures




References
-
- Armani AM, Vahala KJ. Heavy water detection using ultrahigh-Q microcavities. Opt Lett. 2006;31(12):1896–1898. - PubMed
-
- Armani DK, Kippenberg TJ, Spillane SM, Vahala KJ. Ultrahigh-Q toroid microcavity on a chip. Nature. 2003;421(6926):925–928. - PubMed
-
- Arnold S, Khoshsima M, Teraoka I, Holler S, Vollmer F. Shift of whispering-gallery modes in microspheres by protein adsorption. Opt Lett. 2003;28(4):272–274. - PubMed
-
- Bard A. Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. New York: Wiley; 2001.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
