IRF8 regulates myeloid and B lymphoid lineage diversification
- PMID: 18806934
- PMCID: PMC2803682
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-008-8055-8
IRF8 regulates myeloid and B lymphoid lineage diversification
Abstract
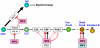
Interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) is a member of the IRF family of transcription factors whose members play critical roles in interferon (IFN) signaling pathways governing the establishment of innate immune responses by myeloid and dendritic cells. IRF8 is also expressed in lymphoid cells and recent studies have documented its involvement in B cell lineage specification, immunoglobulin light chain gene rearrangement, the distribution of mature B cells into the marginal zone and follicular B cell compartment, and the transcriptional regulation of critical elements of the germinal center reaction. Here we review the contributions of IRF8 to B cell development from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and its place in the hierarchical regulatory network governing specification and commitment to the B cell fate.
Figures


References
-
- Busslinger M. Transcriptional control of early B cell development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:55–79. - PubMed
-
- Hardy RR, Kincade PW, Dorshkind K. The protean nature of cells in the B lymphocyte lineage. Immunity. 2007;26:703–14. - PubMed
-
- Medina KL, Pongubala JM, Reddy KL, Lancki DW, Dekoter R, Kieslinger M, et al. Assembling a gene regulatory network for specification of the B cell fate. Dev Cell. 2004;7:607–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

