Alteration of DBP levels in CSF of patients with MS by proteomics analysis
- PMID: 18807170
- PMCID: PMC11505834
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9312-z
Alteration of DBP levels in CSF of patients with MS by proteomics analysis
Abstract
Objective: The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) is still challenging recently due to the lack of a specific diagnostic test. Proteomics analysis was applied to biomarkers discovery and their pathways study.
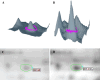
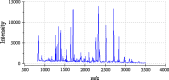
Methods: First, the proteins of CSF from MS patients and control group were analyzed individually with 2D-DIGE technology (two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis). Then, protein spots were found out with DeCyder6.0 software which showed different expression levels in the gel images between the two groups. The information regarding these proteins was collected based on MALDI-TOF/MS and related database searches. Lastly, interaction between these proteins was further analyzed by using Metacore software.
Results: There were 13 proteins that showed more than 1.5-fold difference in expression levels between the two groups. Furthermore, the identification made by MALDI-TOF/MS revealed that one of the most significant differential proteins was DBP (vitamin D-binding protein), which decreased in the experimental group. This result was confirmed by ELISA (P < 0.01). Moreover, network between the 13 proteins were partially got, which showed some biological interactions.
Conclusion: These results support a correlation between the level of DBP and MS. DBP may be a potential useful biomarker for diagnosis or a medicine target for treatment of MS.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Aug;13(8A):1586-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00850.x. Epub 2009 Jul 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19602050 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein in cerebrospinal fluid is associated with multiple sclerosis progression.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Jun;47(3):946-56. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8387-1. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23339019
-
Vitamin D Binding Protein Isoforms and Apolipoprotein E in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Prognostic Biomarkers of Multiple Sclerosis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0129291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129291. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26046356 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker discovery for kidney diseases by mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008 Jul 15;870(2):148-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.10.035. Epub 2007 Nov 1. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18024247 Review.
-
Cancer biomarker discovery for cholangiocarcinoma: the high-throughput approaches.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014 Jun;21(6):388-96. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.68. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014. PMID: 24616382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of protein networks involved in the disease course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, an animal model of multiple sclerosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035544. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22530047 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of vitamin D binding protein in multiple sclerosis.J Neurol. 2011 Mar;258(3):353-8. doi: 10.1007/s00415-010-5797-8. Epub 2010 Nov 2. J Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21042807 Review.
-
Distribution of vitamin D binding protein expressing neurons in the rat hypothalamus.Histochem Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;131(3):365-70. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0540-6. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19034485
-
Vitamin D binding protein in psychiatric and neurological disorders: Implications for diagnosis and treatment.Genes Dis. 2024 Apr 15;11(5):101309. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101309. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 38983447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia-Derived Vitamin D Binding Protein Mediates Synaptic Damage and Induces Depression by Binding to the Neuronal Receptor Megalin.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Feb;12(6):e2410273. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410273. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39716879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams RA, Schachtrup C, Davalos D, Tsigelny I, Akassoglou K (2007) Fibrinogen signal transduction as a mediator and therapeutic target in inflammation: lessons from multiple sclerosis. Curr Med Chem 14(27):2925–2936 - PubMed
-
- Aksungar FB, Topkaya AE, Yildiz Z, Sahin S, Turk U (2008) Coagulation status and biochemical and inflammatory markers in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Neurosci 15:393–397 - PubMed
-
- Brown SJ (2006) The role of vitamin D in multiple sclerosis. Ann Pharmacother 40:1158–1161 - PubMed
-
- Compston A, Confavreux C, Lassmann H, McDonald I, Miller D, Noseworthy J, Smith K, Wekerle H (2006) McAlpine’s multiple sclerosis. Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, p 982
-
- Gomme PT, Bertolini J (2004) Therapeutic potential of vitamin D-binding protein. Trends Biotechnol 22(7):340–345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

