Molecular analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress response after global forebrain ischemia/reperfusion in rats: effect of neuroprotectant simvastatin
- PMID: 18807172
- PMCID: PMC11505799
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9309-7
Molecular analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress response after global forebrain ischemia/reperfusion in rats: effect of neuroprotectant simvastatin
Abstract
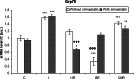
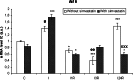
Simvastatin is a cholesterol-lowering agent whose functional significance and neuroprotective mechanism in ischemic brain injury is not yet solved. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of simvastatin on ischemic brain injury. We examined the endoplasmic reticulum stress response (UPR/unfolded protein response), by measuring the mRNA and protein levels of specific genes such as ATF6, GRP78, and XBP1 after 15 min 4-VO ischemia and different times of reperfusion (1, 3, and 24 h). The results from the group of naïve ischemic rats were compared with results from the group of pre-treated animals with simvastatin. The results of the experiments showed significant increase in all genes at the mRNA level in ischemic phase (about 43% for XBP1, 58% for GRP78, and 39% for ATF6 more than control). The protein level of XBP1 was decreased in pre-treated animals at ischemic phase and first hour of reperfusion (about 15% less), and did not reach control levels. The protein levels of GRP78 were maximal at third hour of reperfusion in statin group with a small decrease at 24 h of reperfusion in both groups. The levels of ATF6 mRNA in statin-treated animals was higher in comparison to non-statin animals at the ischemic phase and the third hour of reperfusion (about 35% higher), which was also translated into the higher protein level. This could indicate that one of the main proteins targeted to enhance neuroprotective effect to ER during the first two hours of reperfusion was ATF6 protein, the levels of which were 60% higher than in non-treated animals. These data suggest that simvastatin, in addition to the proposed neuroprotective effect, exerts a neuroprotective role in the attenuation of ER stress response after acute ischemic/reperfusion insult.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats.Neurotox Res. 2010 Feb;17(2):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s12640-009-9110-5. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 19763736
-
Molecular mechanisms leading to neuroprotection/ischemic tolerance: effect of preconditioning on the stress reaction of endoplasmic reticulum.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Sep;29(6-7):917-25. doi: 10.1007/s10571-009-9376-4. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19283468 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress gene induction and protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury in the hearts of transgenic mice with a tamoxifen-regulated form of ATF6.Circ Res. 2006 May 12;98(9):1186-93. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000220643.65941.8d. Epub 2006 Apr 6. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16601230
-
Heat shock proteins in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Exp Neurol. 2025 Aug;390:115284. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2025.115284. Epub 2025 May 1. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40318821 Review.
-
Translation arrest and ribonomics in post-ischemic brain: layers and layers of players.J Neurochem. 2008 Sep;106(6):2288-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05561.x. Epub 2008 Jul 8. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18627434 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Why antidiabetic drugs are potentially neuroprotective during the Sars-CoV-2 pandemic: The focus on astroglial UPR and calcium-binding proteins.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 29;16:905218. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.905218. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35966209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atorvastatin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Dec 15;7(12):4915-23. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25663988 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Statins and Other Cardiovascular Medication on Ischemia-Reperfusion Damage in a Human DIEP Flap Model: Theoretical and Epidemiological Considerations.J Transplant. 2012;2012:504081. doi: 10.1155/2012/504081. Epub 2012 May 9. J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22649712 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin rescues memory and granule cell maturation through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 9;13(4):325. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04784-y. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35397630 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats.Neurotox Res. 2010 Feb;17(2):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s12640-009-9110-5. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 19763736
References
-
- Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A, Mori K (2008) ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct Funct 33:75–89. doi:10.1247/csf.07044 - PubMed
-
- Amin-Hanjan S, Stagliano NE, Yamada M, Huang PL, Liao JK, Moskowitz MA (2001) Mevastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, reduces stroke damage and upregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in mice. Stroke 32:980–986 - PubMed
-
- Aoki M, Tamatani M, Taniguchi M, Yamaguchi A, Bando Y, Kasai K et al (2001) Hypothermic treatment restores glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) expression in ischemic brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 95(1–2):117–128. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(01)00255-8 - PubMed
-
- Balduini W, Mazzoni E, Carloni S, De Simoni MG, Perego C, Sironi L (2003) Prophylactic but not delayed administration of simvastatin protects against long-lasting cognitive and morphological consequences of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, reduces interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factoralpha mRNA induction, and does not affect endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression. Stroke 34:2007–2012. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000080677.24419.88 - PubMed
-
- Bucelli RC, Gonsiorek EA, Kim WY, Bruun D, Rabin RA, Higgins D et al (2008) Statins decrease expression of the proinflammatory neuropeptides calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in sensory neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324(3):1172–1180. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.132795 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

