The inhibitory potencies of monoclonal antibodies to the macrophage adhesion molecule sialoadhesin are greatly increased following PEGylation
- PMID: 18808170
- PMCID: PMC2730630
- DOI: 10.1021/bc800259z
The inhibitory potencies of monoclonal antibodies to the macrophage adhesion molecule sialoadhesin are greatly increased following PEGylation
Abstract
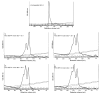
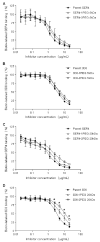
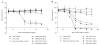
PEGylation of antibodies is known to increase their half-life in systemic circulation, but nothing is known regarding whether PEGylation can improve the inhibitory potency of antibodies against target receptors. In this paper, we have examined this question using antibodies directed to Sialoadhesin (Sn), a macrophage-restricted adhesion molecule that mediates sialic acid dependent binding to different cells. Anti-Sn monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), SER-4 and 3D6, were conjugated to PEG 5 kDa or and PEG 20 kDa, resulting in the incorporation of up to 3 molecules of PEG per mAb molecule. Following purification of PEGylated mAbs by anion exchange chromatography, it was shown that PEGylation had little or no effect on antigen binding activity but led to a dramatic increase in inhibitory potency that was proportional to both the size of the PEG and the degree of derivatization. Thus, PEGylation of antibodies directed to cell surface receptors could be a powerful approach to improve the therapeutic efficacy of antibodies, not only by increasing their half-life in vivo, but also by increasing their inhibitory potency for blocking receptor-ligand interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PEGylation of anti-sialoadhesin monoclonal antibodies enhances their inhibitory potencies without impairing endocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages.Bioconjug Chem. 2009 Feb;20(2):295-303. doi: 10.1021/bc800390g. Bioconjug Chem. 2009. PMID: 19143515
-
Sialoadhesin-positive host macrophages play an essential role in graft-versus-leukemia reactivity in mice.Blood. 1999 Jun 15;93(12):4375-86. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10361136
-
Sialoadhesin, a macrophage sialic acid binding receptor for haemopoietic cells with 17 immunoglobulin-like domains.EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4490-503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06771.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 7925291 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of sialoadhesin as a macrophage recognition molecule in health and disease.Glycoconj J. 1997 Aug;14(5):601-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1018588526788. Glycoconj J. 1997. PMID: 9298693 Review.
-
Sialic acid binding receptors (siglecs) expressed by macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Nov;66(5):705-11. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.5.705. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10577497 Review.
References
-
- Veronese FM, Pasut G. PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today. 2005;10:1451–1458. - PubMed
-
- Fee CJ, Van Alstine JM. PEG-proteins: Reaction engineering and separation issues. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006;61:924–939.
-
- Davis LS, Kavanaugh AF, Nichols LA, Lipsky PE. Induction of persistent T cell hyporesponsiveness in vivo by monoclonal antibody to ICAM-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 1995;154:3525–3537. - PubMed
-
- Soriano A, Salas A, Salas A, Sans M, Gironella M, Elena M, Anderson DC, Pique JM, Panes J. VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1 or MAdCAM-1, immunoblockade ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice. Lab. Invest. 2000;80:1541–1551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

