Identification of a novel protein promoting the colonization and survival of Finegoldia magna, a bacterial commensal and opportunistic pathogen
- PMID: 18808384
- PMCID: PMC2628433
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06439.x
Identification of a novel protein promoting the colonization and survival of Finegoldia magna, a bacterial commensal and opportunistic pathogen
Abstract
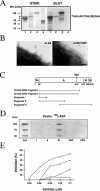
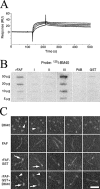
Anaerobic bacteria dominate the human normal microbiota, but strikingly little is known about these commensals. Finegoldia magna is a Gram-positive anaerobe found in the skin and at other non-sterile body surfaces, but it is also an opportunistic pathogen. This study describes a novel protein designated FAF (F. magna adhesion factor) and expressed by more than 90% of F. magna isolates. The protein is present in substantial quantities at the F. magna surface but is also released from the surface. FAF forms large protein aggregates in solution and surface-associated FAF causes bacterial clumping. In skin F. magna bacteria were localized to the epidermis, where they adhere to basement membranes. FAF was found to mediate this adhesion via interactions with BM-40, a basement membrane protein. The biological significance of FAF is further underlined by the observation that it blocks the activity of LL-37, a major human antibacterial peptide. Altogether, the data demonstrate that FAF plays an important role in colonization and survival of F. magna in the human host.
Figures

 ).
).




Similar articles
-
SufA--a novel subtilisin-like serine proteinase of Finegoldia magna.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Dec;153(Pt 12):4208-4218. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/010322-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 18048934
-
Identification of molecular mechanisms used by Finegoldia magna to penetrate and colonize human skin.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Oct;94(2):403-17. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12773. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25164331 Free PMC article.
-
FAF and SufA: proteins of Finegoldia magna that modulate the antibacterial activity of histones.J Innate Immun. 2014;6(3):394-404. doi: 10.1159/000356432. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 24335013 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence arsenal of the most pathogenic species among the Gram-positive anaerobic cocci, Finegoldia magna.Anaerobe. 2016 Dec;42:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Anaerobe. 2016. PMID: 27756620 Review.
-
Adhesion to cellulose by Ruminococcus albus: a combination of cellulosomes and Pil-proteins?FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 Apr 15;185(2):109-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09047.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10754233 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse microbial interactions with the basement membrane barrier.Trends Microbiol. 2012 Mar;20(3):147-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Trends Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22300759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Msb2 shedding protects Candida albicans against antimicrobial peptides.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Feb;8(2):e1002501. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002501. Epub 2012 Feb 2. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22319443 Free PMC article.
-
SufA of the opportunistic pathogen finegoldia magna modulates actions of the antibacterial chemokine MIG/CXCL9, promoting bacterial survival during epithelial inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 23;284(43):29499-508. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025957. Epub 2009 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19628464 Free PMC article.
-
Finegoldia magna, an Anaerobic Gram-Positive Bacterium of the Normal Human Microbiota, Induces Inflammation by Activating Neutrophils.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 29;11:65. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00065. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117109 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the role of cell-wall β-1,3-exoglucanase Xog1p in Candida albicans adhesion by the human antimicrobial peptide LL-37.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021394. Epub 2011 Jun 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21713010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Åkesson P, Cooney J, Kishimoto F, Björck L. Protein H-a novel IgG binding bacterial protein. Mol Immunol. 1990;27:523–531. - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Baschong W, Wrigley NG. Small colloidal gold conjugated to Fab fragments or to immunoglobulin G as high-resolution labels for electron microscopy: a technical overview. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990;14:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Bassetti S, Laifer G, Goy G, Fluckiger U, Frei R. Endocarditis caused by Finegoldia magna (formerly Peptostreptococcus magnus): diagnosis depends on the blood culture system used. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003;47:359–360. - PubMed
-
- Berge A, Björck L. Streptococcal cysteine proteinase releases biologically active fragments of streptococcal surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:9862–9867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

