Caffeine protects against MPTP-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mouse striatum
- PMID: 18808450
- PMCID: PMC3692355
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05697.x
Caffeine protects against MPTP-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mouse striatum
Abstract
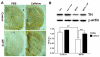
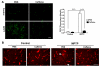
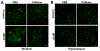
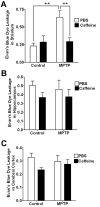
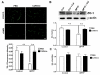
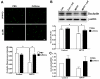
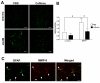
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is important physiologically. Pathologically, BBB disruption has been implicated in a wide spectrum of neurological disorders including Parkinson's disease (PD). Recent studies indicate that caffeine is protective against PD, but by poorly understood mechanisms. Using a MPTP neurotoxin model of PD we tested the hypothesis that the protective actions of caffeine were because of, at least in part, preventing MPTP-induced BBB dysfunction. FVB mice were pre-treated with caffeine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or saline for 7 days prior to initiation of neurotoxin treatments; during the 7 days of neurotoxin treatment, caffeine or saline continued to be administered 10 min before each dose of MPTP (20 mg/kg, i.p.). Striatum (and for some studies hippocampus and cerebral cortex as well) were evaluated for BBB leakage, tight junction protein expression levels, integrity of dopaminergic neurons, and activation of astrocytes and microglia using immunostaining, immunoblotting and real-time PCR techniques. We found that caffeine blocked MPTP-induced decreases in numbers of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive dopaminergic neurons, increases in leakage of Evan's blue dye and FITC-albumin in striatum but not in cerebral cortex or hippocampus, decreases in levels of the tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1, and increases in reactive gliosis. Our results suggest that caffeine might protect against PD and PD-like features in animal models, in part, by stabilizing the BBB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caffeine blocks disruption of blood brain barrier in a rabbit model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Apr 3;5:12. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-12. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18387175 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium butyrate exerts protective effect against Parkinson's disease in mice via stimulation of glucagon like peptide-1.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Oct 15;381:176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.08.3235. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28991675
-
Ulinastatin protects brain against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting MMP-9 and alleviating loss of ZO-1 and occludin proteins in mice.Exp Neurol. 2018 Apr;302:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.12.016. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29291404
-
Methamphetamine transiently increases the blood-brain barrier permeability in the hippocampus: role of tight junction proteins and matrix metalloproteinase-9.Brain Res. 2011 Sep 9;1411:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.013. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21803344
-
Caffeine protects against disruptions of the blood-brain barrier in animal models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S127-41. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1376. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20164568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier Tight Junction in Central Nervous System Disorders.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 6;11:914. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00914. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in understanding substantia nigra hyperechogenicity via transcranial sonography in Parkinson's disease and its clinical implications.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1407860. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1407860. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39091976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Blood-Brain Barrier and Its Intercellular Junctions in Age-Related Brain Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 3;20(21):5472. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215472. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31684130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeine induces neurobehavioral effects through modulating neurotransmitters.Saudi Pharm J. 2020 Apr;28(4):445-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Saudi Pharm J. 2020. PMID: 32273803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cells improve dopaminergic neuron in the MPTP-mice.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jun 1;18(3):970-81. doi: 10.2741/4156. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Hollinger LA, Wolpert EB, Gardner TW. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces rapid phosphorylation of tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occluden 1. A potential mechanism for vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy and tumors. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:23463–23467. - PubMed
-
- Arendash GW, Schleif W, Rezai-Zadeh K, Jackson EK, Zacharia LC, Cracchiolo JR, Shippy D, Tan J. Caffeine protects Alzheimer's mice against cognitive impairment and reduces brain beta-amyloid production. Neuroscience. 2006;142:941–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

