Tv-RIO1 - an atypical protein kinase from the parasitic nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus
- PMID: 18808669
- PMCID: PMC2564912
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-1-34
Tv-RIO1 - an atypical protein kinase from the parasitic nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus
Abstract
Background: Protein kinases are key enzymes that regulate a wide range of cellular processes, including cell-cycle progression, transcription, DNA replication and metabolic functions. These enzymes catalyse the transfer of phosphates to serine, threonine and tyrosine residues, thus playing functional roles in reversible protein phosphorylation. There are two main groups, namely eukaryotic protein kinases (ePKs) and atypical protein kinases (aPKs); RIO kinases belong to the latter group. While there is some information about RIO kinases and their roles in animals, nothing is known about them in parasites. This is the first study to characterise a RIO1 kinase from any parasite.
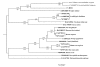
Results: A full-length cDNA (Tv-rio-1) encoding a RIO1 protein kinase (Tv-RIO1) was isolated from the economically important parasitic nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus (Order Strongylida). The uninterrupted open reading frame (ORF) of 1476 nucleotides encoded a protein of 491 amino acids, containing the characteristic RIO1 motif LVHADLSEYNTL. Tv-rio-1 was transcribed at the highest level in the third-stage larva (L3), and a higher level in adult females than in males. Comparison with homologues from other organisms showed that protein Tv-RIO1 had significant homology to related proteins from a range of metazoans and plants. Amino acid sequence identity was most pronounced in the ATP-binding motif, active site and metal binding loop. Phylogenetic analyses of selected amino acid sequence data revealed Tv-RIO1 to be most closely related to the proteins in the species of Caenorhabditis. A structural model of Tv-RIO1 was constructed and compared with the published crystal structure of RIO1 of Archaeoglobus fulgidus (Af-Rio1).
Conclusion: This study provides the first insights into the RIO1 protein kinases of nematodes, and a foundation for further investigations into the biochemical and functional roles of this molecule in biological processes in parasitic nematodes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Feb 7;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/ph10010021. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28178206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trichostrongylus vitrinus (Nematoda: Strongylida): molecular characterization and transcriptional analysis of Tv-stp-1, a serine/threonine phosphatase gene.Exp Parasitol. 2007 Sep;117(1):22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2007.03.008. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Exp Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17490653
-
Genomic characterization of Tv-ant-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans tag-61 homologue from the parasitic nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus.Gene. 2007 Aug 1;397(1-2):12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.03.011. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17512141
-
Structure and activity of the atypical serine kinase Rio1.FEBS J. 2005 Jul;272(14):3698-713. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04796.x. FEBS J. 2005. PMID: 16008568
-
The RIO kinases: an atypical protein kinase family required for ribosome biogenesis and cell cycle progression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1754(1-2):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.07.037. Epub 2005 Sep 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16182620 Review.
Cited by
-
The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Feb 7;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/ph10010021. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28178206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First Evidence of Function for Schistosoma japonicumriok-1 and RIOK-1.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 8;10(7):862. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070862. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358012 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenesis in Strongyloides and related parasitic nematodes: historical perspectives, current functional genomic applications and progress towards gene disruption and editing.Parasitology. 2017 Mar;144(3):327-342. doi: 10.1017/S0031182016000391. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Parasitology. 2017. PMID: 27000743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward understanding the functional role of Ss-RIOK-1, a RIO protein kinase-encoding gene of Strongyloides stercoralis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Aug 7;8(8):e3062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003062. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25101874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanks SK, Hunter T. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification. FASEB J. 1995;9:576–596. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

