Selective lesion of septal cholinergic neurons in rats impairs acquisition of a delayed matching to position T-maze task by delaying the shift from a response to a place strategy
- PMID: 18809473
- PMCID: PMC2649660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.08.016
Selective lesion of septal cholinergic neurons in rats impairs acquisition of a delayed matching to position T-maze task by delaying the shift from a response to a place strategy
Abstract
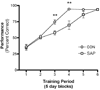
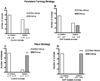
This study tested the hypothesis that septal cholinergic lesions impair acquisition of a delayed matching to position (DMP) T-maze task in male rats by affecting learning strategy. Rats received either the selective cholinergic immunotoxin, 192 IgG-saporin (SAP) or artificial cerebrospinal fluid directly into the medial septum. Two weeks later, animals were trained to acquire the DMP task. SAP-treated rats took significantly longer to acquire the task than corresponding controls. Both SAP-treated and control rats adopted a persistent turn and utilized a response strategy during early periods of training. By the time rats reached criterion the persistent turn was no longer evident, and all rats had shifted to an allocentric strategy, i.e., were relying on extramaze cues to a significant degree. During the acquisition period, SAP-treated rats spent significantly more days showing a persistent turn and using a response strategy than corresponding controls. The added time spent using a response strategy accounted entirely for the added days required to reach criterion among the SAP-treated rats. This suggests that the principal mechanism by which septal cholinergic lesions impair DMP acquisition in male rats is by increasing the predisposition to use a response vs. a place strategy, thereby affecting the ability to switch from one strategy to another.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cholinergic lesions produce task-selective effects on delayed matching to position and configural association learning related to response pattern and strategy.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007 Jul;88(1):19-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2007.03.007. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17449284 Free PMC article.
-
Selective lesion of cholinergic neurons in the medial septum by 192 IgG-saporin impairs learning in a delayed matching to position T-maze paradigm.Brain Res. 2002 Jul 5;943(1):132-41. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02623-9. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12088847
-
Aversive stimulus attenuates impairment of acquisition in a delayed match to position T-maze task caused by a selective lesion of septo-hippocampal cholinergic projections.Brain Res Bull. 2006 May 31;69(6):660-5. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.03.011. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Brain Res Bull. 2006. PMID: 16716835 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selective immunotoxic lesions on learning and memory.Methods Mol Biol. 2001;166:249-65. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-114-0:249. Methods Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11217371 Review. No abstract available.
-
Neonatal 192 IgG-saporin lesion of forebrain cholinergic neurons: focus on the life span?Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003 Sep;27(4):365-76. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(03)00067-8. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003. PMID: 12946689 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural MRI of the basal forebrain as predictor of cognitive response to galantamine in healthy older adults-A randomized controlled double-blinded crossover study.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021 Apr 5;7(1):e12153. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12153. eCollection 2021. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021. PMID: 33842683 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory viral infection in neonatal piglets causes marked microglia activation in the hippocampus and deficits in spatial learning.J Neurosci. 2014 Feb 5;34(6):2120-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2180-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24501353 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the steroid sulfatase inhibitor (p-O-sulfamoyl)-tetradecanoyl tyramine (DU-14) on learning and memory in rats with selective lesion of septal-hippocampal cholinergic tract.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Oct;98(3):303-10. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 23022361 Free PMC article.
-
The utilisation of operant delayed matching and non-matching to position for probing cognitive flexibility and working memory in mouse models of Huntington's disease.J Neurosci Methods. 2016 May 30;265:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.08.022. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Neurosci Methods. 2016. PMID: 26321735 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic treatment with a GPR30 antagonist impairs acquisition of a spatial learning task in young female rats.Horm Behav. 2012 Sep;62(4):367-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Jul 22. Horm Behav. 2012. PMID: 22828404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araugjo DM, Lapchak PA, Robitaille Y, Gauthier S, Quirion R. Differential alteration of various cholinergic markers in cortical and sub-cortical regions of the human brain in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 1988;50:1914–1923. - PubMed
-
- Arkhipov V, Kulesskaja N, Lebedev D. Behavioral perseveration and impairment of long-term memory in rats after intrahippocampal injection of kainic acid in subconvulsive dose, Pharmacology. Biochemistry and Behavior. 2008;88:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Astur RS, Tropp J, Sava S, Constable RT, Markus EJ. Sex differences and correlations in a virtual Morris water task, a virtual radial arm maze, and mental rotation. Behav. Brain Res. 2004;151:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Baxter MG, Bucci DJ, Gorman LK, Wiley RG, Gallagher M. Selective immunotoxic lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic cells: effects on learning and memory in rats. Behav. Neurol. 1995;109:714–722. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa AS. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982;217:408–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

