Neurotransmitter release during delay eyeblink classical conditioning: role of norepinephrine in consolidation and effect of age
- PMID: 18809505
- PMCID: PMC2752948
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.08.008
Neurotransmitter release during delay eyeblink classical conditioning: role of norepinephrine in consolidation and effect of age
Abstract
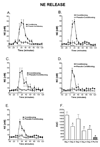
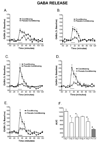
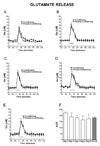
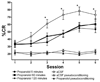
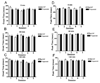
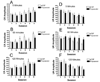
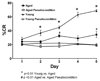
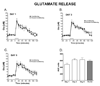
Delay classical eyeblink conditioning (EBC) is an important model of associative, cerebellar-dependent learning. Norepinephrine (NE) plays a significant modulatory role in the acquisition of learning; however, other neurotransmitters are also involved. The goal was to determine whether NE, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate (GLU) release are observed in cerebellar cortex during EBC, and whether such release was selectively associated with training. Further studies examined the role of the beta-noradrenergic receptor in consolidation of the learned response by local infusion of propranolol at 5-120 min following training into the cerebellar cortex. In vivo microdialysis coupled to EBC was performed to examine neurotransmitter release. An increase in the extracellular level of NE was observed during EBC and was maximal on day 1 and diminished in amplitude with subsequent days of training. No changes in baseline NE release were observed in pseudoconditioning indicating that NE release is directly related to the associative learning process. The extracellular levels of GABA were also increased selectively during paired training however, the magnitude of GABA release increased over days of training. GLU release was observed to increase during both paired and unpaired training, suggesting that learning does not occur prior to the information arriving in the cerebellum. When propranolol was administered at either 5-, 60-, or 120-min post-training, there was an inhibition of conditioned responses, these data support the hypothesis that NE is important for consolidation of learning. In another set of experiments we demonstrate that the timing of release of NE, GABA and glutamate are significantly delayed in onset and lengthened in duration in the 22-month-old F344 rats. Over days of training the timing of release becomes closer to the timing of training and this is associated with increased learning of conditioned responses in the aged rats.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cerebellar norepinephrine modulates learning of delay classical eyeblink conditioning: evidence for post-synaptic signaling via PKA.Learn Mem. 2004 Nov-Dec;11(6):732-7. doi: 10.1101/lm.83104. Epub 2004 Nov 10. Learn Mem. 2004. PMID: 15537737 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of beta-noradrenergic receptor blockade on acquisition of eyeblink conditioning in 3-month-old F344 rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002 Sep;78(2):246-57. doi: 10.1006/nlme.2002.4063. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002. PMID: 12431416
-
Post-acquisition release of glutamate and norepinephrine in the amygdala is involved in taste-aversion memory consolidation.Learn Mem. 2012 May 15;19(6):231-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.024703.111. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22589279
-
The neural circuitry and molecular mechanisms underlying delay and trace eyeblink conditioning in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Feb 1;278:307-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25448430 Review.
-
A central role for norepinephrine in the modulation of cerebellar learning tasks.Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev. 2004 Jun;3(2):131-8. doi: 10.1177/1534582304270783. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev. 2004. PMID: 15537989 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebellar sub-divisions differ in exercise-induced plasticity of noradrenergic axons and in their association with resilience to activity-based anorexia.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Jan;222(1):317-339. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1220-2. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27056728 Free PMC article.
-
Purkinje Cell-Specific Knockout of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Impairs Cognitive Behaviors.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jul 29;14:228. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00228. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848620 Free PMC article.
-
Acute aerobic exercise enhances associative learning in regular exercisers but not in non-regular exercisers.Front Behav Neurosci. 2025 Jan 7;18:1515682. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1515682. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39839536 Free PMC article.
-
Trace eyeblink conditioning is associated with changes in synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the cerebellar interpositus nucleus in guinea pigs.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 8;38(3):BSR20170335. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170335. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29051391 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal state-dependent behavioral reflex to an identical sensory input in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 14;9(11):e112927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112927. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25397873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksenov D, Serdyukova N, Irwin K, Bracha V. GABA neurotransmission in the cerebellar interposed nuclei: involvement in classically conditioned eyeblinks and neuronal activity. J.Neurophysiol. 2004;91:719–727. - PubMed
-
- Ardenghi P, Barros D, Izquierdo LA, Bevilaqua L, Schroder N, Quevedo J, Rodrigues C, Madruga M, Medina JH, Izquierdo I. Late and prolonged post-training memory modulation in entorhinal and parietal cortex by drugs acting on the cAMP/protein kinase A signalling pathway. Behav.Pharmacol. 1997;8:745–751. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Kubiak P. Conditioned responses of monkey locus coeruleus neurons anticipate acquisition of discriminative behavior in a vigilance task. Neuroscience. 1997;80:697–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

