Regulatory role of human AP-endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1) in YB-1-mediated activation of the multidrug resistance gene MDR1
- PMID: 18809583
- PMCID: PMC2593380
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00244-08
Regulatory role of human AP-endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1) in YB-1-mediated activation of the multidrug resistance gene MDR1
Abstract
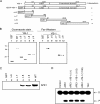
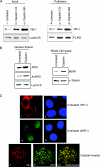
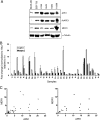
Human AP-endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1), a central enzyme involved in the repair of oxidative base damage and DNA strand breaks, has a second activity as a transcriptional regulator that binds to several trans-acting factors. APE1 overexpression is often observed in tumor cells and confers resistance to various anticancer drugs; its downregulation sensitizes tumor cells to such agents. Because the involvement of APE1 in repairing the DNA damage induced by many of these drugs is unlikely, drug resistance may be linked to APE1's transcriptional regulatory function. Here, we show that APE1, preferably in the acetylated form, stably interacts with Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) and enhances its binding to the Y-box element, leading to the activation of the multidrug resistance gene MDR1. The enhanced MDR1 level due to the ectopic expression of wild-type APE1 but not of its nonacetylable mutant underscores the importance of APE1's acetylation in its coactivator function. APE1 downregulation sensitizes MDR1-overexpressing tumor cells to cisplatin or doxorubicin, showing APE1's critical role in YB-1-mediated gene expression and, thus, drug resistance in tumor cells. A systematic increase in both APE1 and MDR1 expression was observed in non-small-cell lung cancer tissue samples. Thus, our study has established the novel role of the acetylation-mediated transcriptional regulatory function of APE1, making it a potential target for the drug sensitization of tumor cells.
Figures




References
-
- Bargou, R. C., K. Jurchott, C. Wagener, S. Bergmann, S. Metzner, K. Bommert, M. Y. Mapara, K. J. Winzer, M. Dietel, B. Dorken, and H. D. Royer. 1997. Nuclear localization and increased levels of transcription factor YB-1 in primary human breast cancers are associated with intrinsic MDR1 gene expression. Nat. Med. 3447-450. - PubMed
-
- Bobola, M. S., L. S. Finn, R. G. Ellenbogen, J. R. Geyer, M. S. Berger, J. M. Braga, E. H. Meade, M. E. Gross, and J. R. Silber. 2005. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease activity is associated with response to radiation and chemotherapy in medulloblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 117405-7414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
