Association between active genes occurs at nuclear speckles and is modulated by chromatin environment
- PMID: 18809724
- PMCID: PMC2542471
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200803174
Association between active genes occurs at nuclear speckles and is modulated by chromatin environment
Abstract
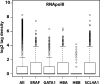
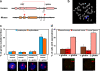
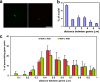
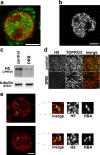
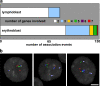
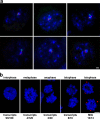
Genes on different chromosomes can be spatially associated in the nucleus in several transcriptional and regulatory situations; however, the functional significance of such associations remains unclear. Using human erythropoiesis as a model, we show that five cotranscribed genes, which are found on four different chromosomes, associate with each other at significant but variable frequencies. Those genes most frequently in association lie in decondensed stretches of chromatin. By replacing the mouse alpha-globin gene cluster in situ with its human counterpart, we demonstrate a direct effect of the regional chromatin environment on the frequency of association, whereas nascent transcription from the human alpha-globin gene appears unaffected. We see no evidence that cotranscribed erythroid genes associate at shared transcription foci, but we do see stochastic clustering of active genes around common nuclear SC35-enriched speckles (hence the apparent nonrandom association between genes). Thus, association between active genes may result from their location on decondensed chromatin that enables clustering around common nuclear speckles.
Figures
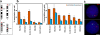
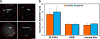
Comment in
-
Gene associations: true romance or chance meeting in a nuclear neighborhood?J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep 22;182(6):1035-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200808121. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18809719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augui, S., G.J. Filion, S. Huart, E. Nora, M. Guggiari, M. Maresca, A.F. Stewart, and E. Heard. 2007. Sensing X chromosome pairs before X inactivation via a novel X-pairing region of the Xic. Science. 318:1632–1636. - PubMed
-
- Bacher, C.P., M. Guggiari, B. Brors, S. Augui, P. Clerc, P. Avner, R. Eils, and E. Heard. 2006. Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Barski, A., S. Cuddapah, K. Cui, T.Y. Roh, D.E. Schones, Z. Wang, G. Wei, I. Chepelev, and K. Zhao. 2007. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Caron, H., B. van Schaik, M. van der Mee, F. Baas, G. Riggins, P. van Sluis, M.C. Hermus, R. van Asperen, K. Boon, P.A. Voute, et al. 2001. The human transcriptome map: clustering of highly expressed genes in chromosomal domains. Science. 291:1289–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

