Sequence and genetic map of Meloidogyne hapla: A compact nematode genome for plant parasitism
- PMID: 18809916
- PMCID: PMC2547418
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805946105
Sequence and genetic map of Meloidogyne hapla: A compact nematode genome for plant parasitism
Abstract
We have established Meloidogyne hapla as a tractable model plant-parasitic nematode amenable to forward and reverse genetics, and we present a complete genome sequence. At 54 Mbp, M. hapla represents not only the smallest nematode genome yet completed, but also the smallest metazoan, and defines a platform to elucidate mechanisms of parasitism by what is the largest uncontrolled group of plant pathogens worldwide. The M. hapla genome encodes significantly fewer genes than does the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (most notably through a reduction of odorant receptors and other gene families), yet it has acquired horizontally from other kingdoms numerous genes suspected to be involved in adaptations to parasitism. In some cases, amplification and tandem duplication have occurred with genes suspected of being acquired horizontally and involved in parasitism of plants. Although M. hapla and C. elegans diverged >500 million years ago, many developmental and biochemical pathways, including those for dauer formation and RNAi, are conserved. Although overall genome organization is not conserved, there are areas of microsynteny that may suggest a primary biological function in nematodes for those genes in these areas. This sequence and map represent a wealth of biological information on both the nature of nematode parasitism of plants and its evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

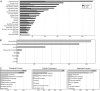
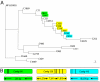
References
-
- Blaxter ML, Bird D. Parasitic nematodes. In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press; 1997. pp. 851–878. - PubMed
-
- Holterman M, et al. Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23:1792–1800. - PubMed
-
- Sasser JN, Freckman DW. A world perspective on nematology: The role of the society. In: Veech JA, Dickson DW, editors. Vistas on Nematology. Hyattsville, MD: Society of Nematologists; 1986. pp. 7–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

