Tet 42, a novel tetracycline resistance determinant isolated from deep terrestrial subsurface bacteria
- PMID: 18809935
- PMCID: PMC2592862
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00640-08
Tet 42, a novel tetracycline resistance determinant isolated from deep terrestrial subsurface bacteria
Abstract
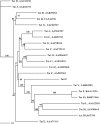
Tet 42, a novel tetracycline resistance determinant from deep subsurface bacteria, was characterized and found to have a 30% sequence similarity to TetA(Z). The protein is a putative efflux pump that shares characteristics with previously characterized pumps, including a divergently transcribed TetR repressor, a conserved GxxSDRxGRR motif, and transmembrane domains.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Clostridium perfringens Tet P determinant comprises two overlapping genes: tetA(P), which mediates active tetracycline efflux, and tetB(P), which is related to the ribosomal protection family of tetracycline-resistance determinants.Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):403-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00320.x. Mol Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8170402
-
Cloning and characterization of a tetracycline resistance determinant present in Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58.J Bacteriol. 1999 Jan;181(2):618-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.2.618-626.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 9882678 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the interdomain loop region of the tetA(A) tetracycline resistance gene increase efflux of minocycline and glycylcyclines.Microb Drug Resist. 2000 Winter;6(4):277-82. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2000.6.277. Microb Drug Resist. 2000. PMID: 11272255
-
Mechanisms underlying expression of Tn10 encoded tetracycline resistance.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:345-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.002021. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7826010 Review.
-
Functions of tetracycline efflux proteins that do not involve tetracycline.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Apr;3(2):237-46. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11321579 Review.
Cited by
-
Efflux-mediated resistance identified among norfloxacin resistant clinical strains of group B Streptococcus from South Korea.Epidemiol Health. 2014 Oct 11;36:e2014022. doi: 10.4178/epih/e2014022. eCollection 2014. Epidemiol Health. 2014. PMID: 25322878 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Presence and Phage-Mediated Transfer of ARGs in Biofilms.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 26;13(5):997. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13050997. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unfolding the collective functional potential of a synergistic multispecies community through genotypic and phenotypic analyses.Biofilm. 2025 May 24;10:100290. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2025.100290. eCollection 2025 Dec. Biofilm. 2025. PMID: 40657038 Free PMC article.
-
The tetracycline resistome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Feb;67(3):419-31. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0172-6. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 19862477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid antimicrobial susceptibility test for Bacillus anthracis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jul;54(7):2793-800. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00247-10. Epub 2010 May 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20439614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barona-Gómez, F., S. Lautru, F. X. Francou, P. Leblond, J. L. Pernodet, and G. L. Challis. 2006. Multiple biosynthetic and uptake systems mediate siderophore-dependent iron acquisition in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877. Microbiology 152:3355-3366. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. G., and D. L. Balkwill. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from the deep terrestrial subsurface. Microb. Ecol., in press. - PubMed
-
- CLSI. 2003. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacteria that grow aerobically, CLSI document M7-A6, vol. 23, 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Reference deleted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

