Population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in young infants
- PMID: 18809946
- PMCID: PMC2573107
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00569-08
Population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in young infants
Abstract
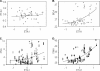
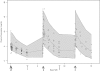
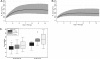
Fluconazole is being increasingly used to prevent and treat invasive candidiasis in neonates, yet dosing is largely empirical due to the lack of adequate pharmacokinetic (PK) data. We performed a multicenter population PK study of fluconazole in 23- to 40-week-gestation infants less than 120 days of age. We developed a population PK model using nonlinear mixed effect modeling (NONMEM) with the NONMEM algorithm. Covariate effects were predefined and evaluated based on estimation precision and clinical significance. We studied fluconazole PK in 55 infants who at enrollment had a median (range) weight of 1.02 (0.440 to 7.125) kg, a gestational age at birth (BGA) of 26 (23 to 40) weeks, and a postnatal age (PNA) of 2.3 (0.14 to 12.6) weeks. The final data set contained 357 samples; 217/357 (61%) were collected prospectively at prespecified time intervals, and 140/357 (39%) were scavenged from discarded clinical specimens. Fluconazole population PK was best described by a one-compartment model with covariates normalized to median values. The population mean clearance (CL) can be derived for this population by the equation CL (liter/h) equals 0.015 . (weight/1)(0.75) . (BGA/26)(1.739) . (PNA/2)(0.237) . serum creatinine (SCRT)(-4.896) (when SCRT is >1.0 mg/dl), and using a volume of distribution (V) (liter) of 1.024 . (weight/1). The relative standard error around the fixed effects point estimates ranged from 3 to 24%. CL doubles between birth and 28 days of age from 0.008 to 0.016 and from 0.010 to 0.022 liter/kg/h for typical 24- and 32-week-gestation infants, respectively. This population PK model of fluconazole discriminated the impact of BGA, PNA, and creatinine on drug CL. Our data suggest that dosing in young infants will require adjustment for BGA and PNA to achieve targeted systemic drug exposures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole for prevention or treatment of invasive candidiasis in Chinese young infants.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;397(11):8853-8862. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03184-7. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38850301
-
Population pharmacokinetics of metronidazole evaluated using scavenged samples from preterm infants.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Apr;56(4):1828-37. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06071-11. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22252819 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Fluconazole in Premature Infants with Birth Weights Less than 750 Grams.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5539-45. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00963-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27401564 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Use of fluconazole in children less than 1 year old: review].Mycoses. 1998;41 Suppl 1:61-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1998.tb00586.x. Mycoses. 1998. PMID: 9717389 Review. German.
-
Fluconazole pharmacokinetics and safety in premature infants.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(27):4617-20. doi: 10.2174/092986712803306367. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22876898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical aspects of invasive candidiasis in paediatric patients.Drugs. 2009;69 Suppl 1:45-50. doi: 10.2165/11315620-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19877734 Review.
-
Changes in individual drug-independent system parameters during virtual paediatric pharmacokinetic trials: introducing time-varying physiology into a paediatric PBPK model.AAPS J. 2014 May;16(3):568-76. doi: 10.1208/s12248-014-9592-9. Epub 2014 Apr 4. AAPS J. 2014. PMID: 24700271 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic studies in infants using minimal-risk study designs.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(4):350-8. doi: 10.2174/1574884709666140520153308. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24844642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing operational efficiencies in early phase trials: The Pediatric Trials Network experience.Contemp Clin Trials. 2016 Mar;47:376-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Contemp Clin Trials. 2016. PMID: 26968616 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Fluconazole Dosing for the Prevention and Treatment of Invasive Candidiasis Based on the Pharmacokinetics of Fluconazole in Critically Ill Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01554-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01554-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33361296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, B. J., and N. H. G. Holford. 2008. Mechanism-based concepts of size and maturity in pharmacokinetics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 48:303-332. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin, D. K., E. DeLong, C. M. Cotten, H. P. Garges, W. J. Steinbach, and R. H. Clark. 2004. Mortality following blood culture in premature infants: increased with Gram-negative bacteremia and candidemia, but not Gram-positive bacteremia. J. Perinatol. 24:175-180. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin, D. K., Jr., E. R. DeLong, W. J. Steinbach, C. M. Cotton, T. J. Walsh, and R. H. Clark. 2003. Empirical therapy for neonatal candidemia in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 112:543-547. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin, D. K., Jr., H. Garges, and W. J. Steinbach. 2003. Candida bloodstream infection in neonates. Semin. Perinatol. 27:375-383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

