Separation of Hepatitis C genotype 4a into IgG-depleted and IgG-enriched fractions reveals a unique quasispecies profile
- PMID: 18811965
- PMCID: PMC2561023
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-103
Separation of Hepatitis C genotype 4a into IgG-depleted and IgG-enriched fractions reveals a unique quasispecies profile
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) circulates in an infected individual as a heterogeneous mixture of closely related viruses called quasispecies. The E1/E2 region of the HCV genome is hypervariable (HVR1) and is targeted by the humoral immune system. Hepatitis C virions are found in two forms: antibody associated or antibody free. The objective of this study was to investigate if separation of Hepatitis C virions into antibody enriched and antibody depleted fractions segregates quasispecies populations into distinctive swarms.
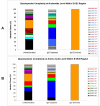
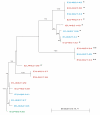
Results: A HCV genotype 4a specimen was fractionated into IgG-depleted and IgG-enriched fractions by use of Albumin/IgG depletion spin column. Clonal analysis of these two fractions was performed and then compared to an unfractionated sample. Following sequence analysis it was evident that the antibody depleted fraction was significantly more heterogeneous than the antibody enriched fraction, revealing a unique quasispecies profile. An in-frame 3 nt insertion was observed in 26% of clones in the unfractionated population and in 64% of clones in the IgG-depleted fraction. In addition, an in-frame 3 nt indel event was observed in 10% of clones in the unfractionated population and in 9% of clones in the IgG-depleted fraction. Neither of these latter events, which are rare occurrences in genotype 4a, was identified in the IgG-enriched fraction.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the homogeneity of the IgG-enriched species is postulated to represent a sequence that was strongly recognised by the humoral immune system at the time the sample was obtained. The heterogeneous nature of the IgG-depleted fraction is discussed in the context of humoral escape.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

