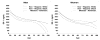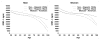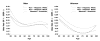Race/ethnic variation in serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in US adults
- PMID: 18812263
- PMCID: PMC2702997
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2008.08.005
Race/ethnic variation in serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in US adults
Abstract
Objectives: The IGF axis plays a significant role in normal growth and development and variation in IGFs is associated with health outcomes. Past studies report variation in IGF levels among race/ethnic groups known to differ in disease incidence. This paper reports on race/ethnic variation in serum levels of IGF-I and IGF-BP3 in a nationally representative and ethnically diverse sample of US adults.
Design: Serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 levels from the fasting subsample (n = 6061) of respondents to the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (NHANES III) were analyzed using an IGF-I ELISA (Diagnostic Systems Laboratory (DSL) 10-5600) and an IGFBP-3 IRMA (DSL 6600). The NHANES is a combined examination and interview survey of a nationally representative sample of US adults. Regression analyses were used to estimate cross-sectional associations between the IGF axis and demographic variables.
Results: In unadjusted analyses, serum IGF-I levels were higher in males than in females, and IGFBP-3 levels were higher in females than in males. Both analytes were lower in older adults. Univariate analyses indicate that serum levels of IGF-I are lower in female Non-Hispanic Whites (NHW) (256 [4.9]) and Hispanics (249 [6.6]) than in Non-Hispanic Blacks (NHB) (281 [4.9]). However, in males, IGF levels in NHWs (287 [3.6]) and NHBs (284 [4.3]) are similar and levels in Mexican-Americans are only moderately reduced (265 [3.4]). Notably, NHB's have the highest molar ratio of IGF-I:IGFBP-3 at all ages. After adjustment for age and BMI, gender and race/ethnicity differences persist.
Conclusions: These cross-sectional data support exploration of the IGF axis as an explanation for some race/ethnic differences in cancer incidence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anthropometric correlates of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels by race/ethnicity and gender.Ann Epidemiol. 2009 Dec;19(12):841-9. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2009.08.005. Ann Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19944347 Free PMC article.
-
Serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF binding protein-3 in relation to breast cancer among Hispanic and white, non-Hispanic women in the US Southwest.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Jun;121(3):661-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0609-5. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 19888649 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional reference regions for IGF-I, IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-3 concentrations in serum of healthy adults.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008 Dec;18(6):506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008. PMID: 18550406
-
Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-I binding protein-3: quality control for studies of stored serum.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007 May;16(5):1017-22. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0044. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007. PMID: 17507631
-
Relationship between serum circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and liver fat in the United States.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Mar;29(3):589-96. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12437. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24716226 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endogenous IGFBP-3 regulates excess collagen expression in intestinal smooth muscle cells of Crohn's disease strictures.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Jan;17(1):193-201. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21351. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011. PMID: 20848532 Free PMC article.
-
Serum IGF-I and C-reactive protein in healthy black and white young men: the CARDIA male hormone study.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009 Oct;19(5):420-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2008.12.002. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009. PMID: 19138871 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of IGF1/IGFBP3 Molar Ratio as an Effective Tool for Assessing the Safety of Growth Hormone Therapy in Small-for-gestational-age, Growth Hormone-Deficient and Prader-Willi Children.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2019 Sep 3;11(3):253-261. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2018.0277. Epub 2019 Feb 14. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30759961 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling Complete Blood Count and Steroidomics to Track Low Doses Administration of Recombinant Growth Hormone: An Anti-Doping Perspective.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 10;8:683675. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.683675. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34179089 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities at presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and survival in African American men, affected by prostate cancer.Prostate. 2011 Jun 15;71(9):985-97. doi: 10.1002/pros.21314. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Prostate. 2011. PMID: 21541975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- LeRoith D, McGuinness M, Shemer J, et al. Insulin-like growth factors. Biol Signals. 1992;1:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Tatar M, Bartke A, Antebi A. The endocrine regulation of aging by insulin-like signals. Science. 2003;299:1346–1351. - PubMed
-
- Rosen CJ. Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins: clinical implications. Clin Chem. 1999;45:1384–1390. - PubMed
-
- Juul A. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding proteins in health and disease. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2003;13:113–170. - PubMed
-
- Juul A, Scheike T, Davidsen M, Gyllenborg J, Jorgensen T. Low serum insulin-like growth factor I is associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease: a population-based case-control study. Circulation. 2002;106:939–944. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous