Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: risk factors for failure over 25 years
- PMID: 18813892
- PMCID: PMC2650042
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0506-y
Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: risk factors for failure over 25 years
Abstract
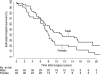
Many early metal-on-polyethylene hip resurfacing arthroplasty designs were abandoned after reports of high short-term and midterm failure rates. To investigate factors associated with failure, we retrospectively reviewed our experience with early-design hip resurfacing implants in 75 patients during a 25-year period (median followup, 7.9 years; range, 0.1-25.2 years). Implant failure was defined as revision for any reason. One of 75 patients was lost to followup. The estimated rate of implant survival was 73% at 5 years, 34% at 10 years, 27% at 15 years, 12% at 20 years, and 8% at 25 years. Of the many clinical and radiographic factors considered, only age, implant type, and gender were associated with implant survival independent of other variables considered. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty showed poor overall long-term survival in this series. Particular attention should be paid to the identified risk factors as long-term followup data become available for modern designs.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures




References
-
- Amstutz HC, Ball ST, Le Duff MJ, Dorey FJ. Resurfacing THA for patients younger than 50 years: results of 2- to 9-year followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Amstutz HC, Beaule PE, Dorey FJ, Le Duff MJ, Campbell PA, Gruen TA. Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty: two to six-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:28–39. - PubMed
-
- Amstutz HC, Campbell P, Nasser S, Kossovsky N. Modes of failure of surface replacements. In: Amstutz HC, ed. Hip Arthroplasty. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 1991:507–534.
-
- Amstutz HC, Campbell PA, Le Duff MJ. Fracture of the neck of the femur after surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1874–1877. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

