Hepatitis C infection and risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 18814931
- PMCID: PMC2642971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.08.006
Hepatitis C infection and risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background/aims: Several studies found hepatitis C (HCV) increases risk of Type II diabetes mellitus (DM). However, others found no or only sub-group specific excess risk. We performed meta-analyses to examine whether HCV infection does increase DM risk in comparison to the general population and in other sub-groups with increased liver disease rates including with hepatitis B (HBV).
Methods: We followed standard guidelines for performance of meta-analyses. Two independent investigators identified eligible studies through structured keyword searches in relevant databases including PubMed.
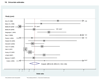
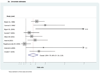
Results: We identified 34 eligible studies. Pooled estimators indicated significant DM risk in HCV-infected cases in comparison to non-infected controls in both retrospective (OR(adjusted)=1.68, 95% CI 1.15-2.20) and prospective studies (HR(adjusted)=1.67, 95% CI 1.28-2.06). Excess risk was also observed in comparison to HBV-infected controls (OR(adjusted)=1.80, 95% CI 1.20-1.40) with suggestive excess observed in HCV+/HIV+ cases in comparison to HIV+ controls (OR(unadjusted)=1.82, 95% CI 1.27-2.38).
Conclusions: Our finding of excess DM risk with HCV infection in comparison to non-infected controls is strengthened by consistency of results from both prospective and retrospective studies. The excess risk observed in comparison to HBV-infected controls suggests a potential direct viral role in promoting DM risk, but this needs to be further examined.
Figures




References
-
- NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002;19:1–46. - PubMed
-
- Zignego AL, Ferri C, Pileri SA, Caini P, Bianchi FB. Extrahepatic manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus infection: a general overview and guidelines for a clinical approach. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39:2–17. - PubMed
-
- Romero-Gomez M, Del Mar Viloria M, Andrade RJ, Salmeron J, Diago M, Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, et al. Insulin resistance impairs sustained response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, Bandara P, Byth K, Kench JG, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and fibrosis progression [corrected] Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1695–1704. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli A, Ferri C, Fallahi P, Pampana A, Ferrari SM, Goglia F, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection: evidence for an association with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2548–2550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

