Toward realistic and practical ideal observer (IO) estimation for the optimization of medical imaging systems
- PMID: 18815105
- PMCID: PMC2739397
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2008.924641
Toward realistic and practical ideal observer (IO) estimation for the optimization of medical imaging systems
Abstract
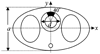
The ideal observer (IO) employs complete knowledge of the available data statistics and sets an upper limit on observer performance on a binary classification task. However, the IO test statistic cannot be calculated analytically, except for cases where object statistics are extremely simple. Kupinski have developed a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) based technique to compute the IO test statistic for, in principle, arbitrarily complex objects and imaging systems. In this work, we applied MCMC to estimate the IO test statistic in the context of myocardial perfusion SPECT (MPS). We modeled the imaging system using an analytic SPECT projector with attenuation, distant-dependent detector-response modeling and Poisson noise statistics. The object is a family of parameterized torso phantoms with variable geometric and organ uptake parameters. To accelerate the imaging simulation process and thus enable the MCMC IO estimation, we used discretized anatomic parameters and continuous uptake parameters in defining the objects. The imaging process simulation was modeled by precomputing projections for each organ for a finite number of discretely-parameterized anatomic parameters and taking linear combinations of the organ projections based on continuous sampling of the organ uptake parameters. The proposed method greatly reduces the computational burden and allows MCMC IO estimation for a realistic MPS imaging simulation. We validated the proposed IO estimation technique by estimating IO test statistics for a large number of input objects. The properties of the first- and second-order statistics of the IO test statistics estimated using the MCMC IO estimation technique agreed well with theoretical predictions. Further, as expected, the IO had better performance, as measured by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, than the Hotelling observer. This method is developed for SPECT imaging. However, it can be adapted to any linear imaging system.
Figures



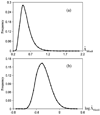


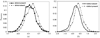
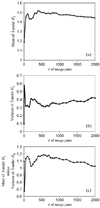

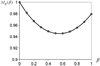
Similar articles
-
Approximating the Ideal Observer and Hotelling Observer for Binary Signal Detection Tasks by Use of Supervised Learning Methods.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019 Oct;38(10):2456-2468. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2911211. Epub 2019 Apr 15. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30990425 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of energy window for 90Y bremsstrahlung SPECT imaging for detection tasks using the ideal observer with model-mismatch.Med Phys. 2013 Jun;40(6):062502. doi: 10.1118/1.4805095. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23718607 Free PMC article.
-
Ideal-observer performance under signal and background uncertainty.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2003 Jul;18:342-53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-45087-0_29. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2003. PMID: 15344470 Clinical Trial.
-
Automatic estimation of the noise variance from the histogram of a magnetic resonance image.Phys Med Biol. 2007 Mar 7;52(5):1335-48. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/5/009. Epub 2007 Feb 8. Phys Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17301458 Review.
-
A brief history about analytic tools in medical imaging: splines, wavelets, singularities and partial differential equations.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:3474-80. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353079. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18002745 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of energy window and evaluation of scatter compensation methods in myocardial perfusion SPECT using the ideal observer with and without model mismatch and an anthropomorphic model observer.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2015 Jan;2(1):015502. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.2.1.015502. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2015. PMID: 26029730 Free PMC article.
-
Approximating the Ideal Observer and Hotelling Observer for Binary Signal Detection Tasks by Use of Supervised Learning Methods.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019 Oct;38(10):2456-2468. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2911211. Epub 2019 Apr 15. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30990425 Free PMC article.
-
Ideal-Observer Computation with anthropomorphic phantoms using Markov chain Monte Carlo.Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2022 Mar;2022:10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761579. doi: 10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761579. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36388622 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient estimation of ideal-observer performance in classification tasks involving high-dimensional complex backgrounds.J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2009 Nov;26(11):B59-71. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.26.000B59. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2009. PMID: 19884916 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of an Adaptive SPECT System with the Scanning Linear Estimator.IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2017 Sep;1(5):435-443. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2017.2715041. Epub 2017 Jun 13. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29276799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rolland JP, Barrett HH. Effect of random background inhomogeneity on observer detection performance. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A, Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 1992;vol. 9:649–658. - PubMed
-
- Gross KA, Kupinski MA, Hesterman JY. A fast model of a multiple-pinhole SPECT imaging system. presented at the SPIE Med. Imag. Conf.; San Diego, CA. 2005.
-
- Gross KA, Kupinski MA, Peterson TE, Clarkson E. Optimizing a multiple-pinhole SPECT system using the ideal observer. presented at the SPIE Med. Imag.; San Diego, CA. 2003.
-
- Metropolis N, Rosenbluth AW, Rosenbluth MN, Teller AH, Teller E. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953;vol. 21:1087–1092.

