Numbers, densities, and colocalization of AMPA- and NMDA-type glutamate receptors at individual synapses in the superficial spinal dorsal horn of rats
- PMID: 18815255
- PMCID: PMC3844880
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1551-08.2008
Numbers, densities, and colocalization of AMPA- and NMDA-type glutamate receptors at individual synapses in the superficial spinal dorsal horn of rats
Abstract
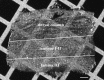
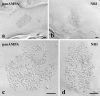
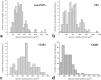
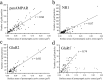
Ionotropic glutamate receptors play important roles in spinal processing of nociceptive sensory signals and induction of central sensitization in chronic pain. Here we applied highly sensitive freeze-fracture replica labeling to laminae I-II of the spinal dorsal horn of rats and investigated the numbers, densities, and colocalization of AMPA- and NMDA-type glutamate receptors at individual postsynaptic membrane specializations with a high resolution. All glutamatergic postsynaptic membranes in laminae I-II expressed AMPA receptors, and most of them (96%) were also immunoreactive for the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors. The numbers of gold particles for AMPA and NMDA receptors at individual postsynaptic membranes showed a linear correlation with the size of postsynaptic membrane specializations and varied in the range of 8-214 and 5-232 with median values of 37 and 28, whereas their densities varied in the range of 325-3365/microm(2) and 102-2263/microm(2) with median values of 1115/microm(2) and 777/microm(2), respectively. Virtually all (99%) glutamatergic postsynaptic membranes expressed GluR2, and most of them (87%) were also immunoreactive for GluR1. The numbers of gold particles for pan-AMPA, NR1, and GluR2 subunits showed a linear correlation with the size of postsynaptic surface areas. Concerning GluR1, there may be two populations of synapses with high and low GluR1 densities. In synapses larger than 0.1 microm(2), GluR1 subunits were recovered in very low numbers. Differential expression of GluR1 and GluR2 subunits suggests regulation of AMPA receptor subunit composition by presynaptic mechanism.
Figures


References
-
- Albuquerque C, Lee CJ, Jackson AC, MacDermott AB. Subpopulations of GABAergic and non-GABAergic rat dorsal horn neurons express Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2758–2766. - PubMed
-
- Antal M, Kraftsik R, Székely G, van der Loos H. Synapses on motoneuron dendrites in the brachial section of the frog spinal cord: a computer-aided electron microscopic study of cobalt-filled cells. J Neurocytol. 1992;21:34–49. - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Doubell TP, Moore KA, Woolf CJ. Silent NMDA receptor-mediated synapses are developmentally regulated in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Molnár E, McIlhinney RA, Somogyi P. High-resolution immunogold localization of AMPA type glutamate receptor subunits at synaptic and non-synaptic sites in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1995;69:1031–1055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
