Cellular and molecular basis of deiodinase-regulated thyroid hormone signaling
- PMID: 18815314
- PMCID: PMC2647704
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2008-0019
Cellular and molecular basis of deiodinase-regulated thyroid hormone signaling
Abstract
The iodothyronine deiodinases initiate or terminate thyroid hormone action and therefore are critical for the biological effects mediated by thyroid hormone. Over the years, research has focused on their role in preserving serum levels of the biologically active molecule T(3) during iodine deficiency. More recently, a fascinating new role of these enzymes has been unveiled. The activating deiodinase (D2) and the inactivating deiodinase (D3) can locally increase or decrease thyroid hormone signaling in a tissue- and temporal-specific fashion, independent of changes in thyroid hormone serum concentrations. This mechanism is particularly relevant because deiodinase expression can be modulated by a wide variety of endogenous signaling molecules such as sonic hedgehog, nuclear factor-kappaB, growth factors, bile acids, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, as well as a growing number of xenobiotic substances. In light of these findings, it seems clear that deiodinases play a much broader role than once thought, with great ramifications for the control of thyroid hormone signaling during vertebrate development and metamorphosis, as well as injury response, tissue repair, hypothalamic function, and energy homeostasis in adults.
Figures
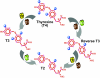

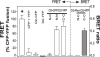
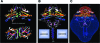
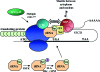
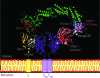
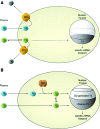
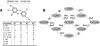
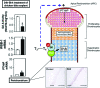

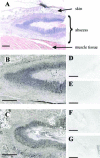

References
-
- Gross J, Pitt-Rivers R 1952 The identification of 3,5, 3′-L-triiodothyronine in human plasma. Lancet 1:439 - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, Koenig RJ 2000 Gene regulation by thyroid hormone. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:207–211 - PubMed
-
- Yen PM, Ando S, Feng X, Liu Y, Maruvada P, Xia X 2006 Thyroid hormone action at the cellular, genomic and target gene levels. Mol Cell Endocrinol 246:121–127 - PubMed
-
- Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR 2002 Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev 23:38–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK076099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK064643/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK078476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076117/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064643/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK78560/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK65055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK058538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK76117/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

