Gedunin, a novel hsp90 inhibitor: semisynthesis of derivatives and preliminary structure-activity relationships
- PMID: 18816111
- PMCID: PMC2850591
- DOI: 10.1021/jm8007486
Gedunin, a novel hsp90 inhibitor: semisynthesis of derivatives and preliminary structure-activity relationships
Abstract
Gedunin (1), a tetranortriterpenoid isolated from the Indian neem tree ( Azadirachta indica), was recently shown to manifest anticancer activity via inhibition of the 90 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp90) folding machinery and to induce the degradation of Hsp90-dependent client proteins similar to other Hsp90 inhibitors. The mechanism of action by which gedunin induces client protein degradation remains undetermined, however, prior studies have demonstrated that it does not bind competitively versus ATP. In an effort to further probe the mechanism of action, 19 semisynthetic derivatives of gedunin were prepared and their antiproliferative activity against MCF-7 and SkBr3 breast cancer cells determined. Although no compound was found to exhibit antiproliferative activity more effective than the natural product, functionalities critical for antiproliferative activity have been identified.
Figures
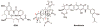


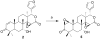


References
-
- Borst P, Jonkers J, Roftenberg S. What makes tumors multidrug resistant? Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2782–2787. - PubMed
-
- Nibili S, Landini I, Giglioni B, Mini E. Pharmacological strategies for overcoming multidrug resistance. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:861–879. - PubMed
-
- Duesberg P, Li R, Sachs R, Fabarius A, Upender M, Hehlmann R. Cancer drug resistance: the central role of the karyotype. Drug Resist Updates. 2007;10:51–58. - PubMed
-
- Nooter K, Stoter G. Molecular mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Pathol, Res Pract. 1996;192:768–780. - PubMed
-
- Neckers L. Heat shock protein 90: the cancer chaperone. J Biosci. 2007;32:517–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

