Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats
- PMID: 18817471
- PMCID: PMC3407669
- DOI: 10.2217/17435889.3.5.703
Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats
Abstract
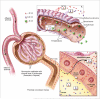
Nanoparticles possess enormous potential as diagnostic imaging agents and hold promise for the development of multimodality agents with both imaging and therapeutic capabilities. Yet, some of the most promising nanoparticles demonstrate prolonged tissue retention and contain heavy metals. This presents serious concerns for toxicity. The creation of nanoparticles with optimal clearance characteristics will minimize toxicity risks by reducing the duration of exposure to these agents. Given that many nanoparticles possess easily modifiable surface and interior chemistry, if nanoparticle characteristics associated with optimal clearance from the body were well established, it would be feasible to design and create agents with more favorable clearance properties. This article presents a thorough discussion of the physiologic aspects of nanoparticle clearance, focusing on renal mechanisms, and provides an overview of current research investigating clearance of specific types of nanoparticles and nano-sized macromolecules, including dendrimers, quantum dots, liposomes and carbon, gold and silica-based nanoparticles.
Figures

References
-
- Hagens WI, Oomen AG, de Jong WH, Cassee FR, Sips AJ. What do we (need to) know about the kinetic properties of nanoparticles in the body? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;49:217–29. - PubMed
-
- Ballou B, Ernst LA, Andreko S, Harper T, Fitzpatrick JA, Waggoner AS, Bruchez MP. Sentinel lymph node imaging using quantum dots in mouse tumor models. Bioconjug Chem. 2007 Mar-Apr;18:389–96. - PubMed
-
- Csortos C, Kolosova I, Verin AD. Regulation of vascular endothelial cell barrier function and cytoskeleton structure by protein phosphatases of the PPP family. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Oct;293:L843–54. - PubMed
-
- Chapman AP, Antoniw P, Spitali M, West S, Stephens S, King DJ. Therapeutic antibody fragments with prolonged in vivo half-lives. Nat Biotechnol. 1999 Aug;17:780–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
