Structural biology of shared cytokine receptors
- PMID: 18817510
- PMCID: PMC3981547
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090616
Structural biology of shared cytokine receptors
Abstract
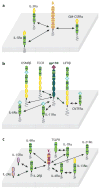
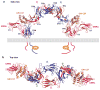
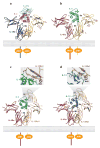
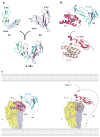
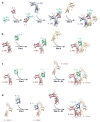
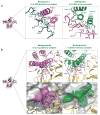
Recent structural information for complexes of cytokine receptor ectodomains bound to their ligands has significantly expanded our understanding of the macromolecular topology and ligand recognition mechanisms used by our three principal shared cytokine signaling receptors-gp130, gamma(c), and beta(c). The gp130 family receptors intricately coordinate three structurally unique cytokine-binding sites on their four-helix bundle cytokine ligands to assemble multimeric signaling complexes. These organizing principles serve as topological blueprints for the entire gp130 family of cytokines. Novel structures of gamma(c) and beta(c) complexes show us new twists, such as the use of a nonstandard sushi-type alpha receptors for IL-2 and IL-15 in assembling quaternary gamma(c) signaling complexes and an antiparallel interlocked dimer in the GM-CSF signaling complex with beta(c). Unlike gp130, which appears to recognize vastly different cytokine surfaces in chemically unique fashions for each ligand, the gamma(c)-dependent cytokines appear to seek out some semblance of a knobs-in-holes shape recognition code in order to engage gamma(c) in related fashions. We discuss the structural similarities and differences between these three shared cytokine receptors, as well as the implications for transmembrane signaling.
Figures
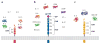
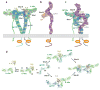

References
-
- Garcia KC, editor. Advances in Protein Chemistry. Vol. 68. London/San Diego: Academic; 2004. p. 506.
-
- Dechant G, Barde YA. The neurotrophin receptor p75(NTR): novel functions and implications for diseases of the nervous system. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:1131–36. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:383–94. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph MG, Stanfield RL, Wilson IA. How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:419–66. - PubMed
-
- Strong RK. Asymmetric ligand recognition by the activating natural killer cell receptor NKG2D, a symmetric homodimer. Mol Immunol. 2002;38:1029–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

