Developmental and diurnal dynamics of Pax4 expression in the mammalian pineal gland: nocturnal down-regulation is mediated by adrenergic-cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signaling
- PMID: 18818287
- PMCID: PMC2646524
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-0882
Developmental and diurnal dynamics of Pax4 expression in the mammalian pineal gland: nocturnal down-regulation is mediated by adrenergic-cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signaling
Abstract
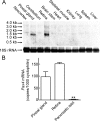
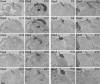
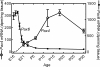
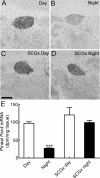
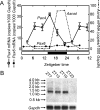
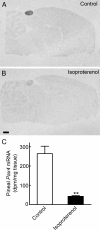
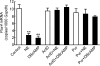
Pax4 is a homeobox gene that is known to be involved in embryonic development of the endocrine pancreas. In this tissue, Pax4 counters the effects of the related protein, Pax6. Pax6 is essential for development of the pineal gland. In this study we report that Pax4 is strongly expressed in the pineal gland and retina of the rat. Pineal Pax4 transcripts are low in the fetus and increase postnatally; Pax6 exhibits an inverse pattern of expression, being more strongly expressed in the fetus. In the adult the abundance of Pax4 mRNA exhibits a diurnal rhythm in the pineal gland with maximal levels occurring late during the light period. Sympathetic denervation of the pineal gland by superior cervical ganglionectomy prevents the nocturnal decrease in pineal Pax4 mRNA. At night the pineal gland is adrenergically stimulated by release of norepinephrine from the sympathetic innervation; here, we found that treatment with adrenergic agonists suppresses pineal Pax4 expression in vivo and in vitro. This suppression appears to be mediated by cAMP, a second messenger of norepinephrine in the pineal gland, based on the observation that treatment with a cAMP mimic reduces pineal Pax4 mRNA levels. These findings suggest that the nocturnal decrease in pineal Pax4 mRNA is controlled by the sympathetic neural pathway that controls pineal function acting via an adrenergic-cAMP mechanism. The daily changes in Pax4 expression may influence gene expression in the pineal gland.
Figures
References
-
- Chi N, Epstein JA 2002 Getting your Pax straight: Pax proteins in development and disease. Trends Genet 18:41–47 - PubMed
-
- Estivill-Torrús G, Vitalis T, Fernández-Llebrez P, Price DJ 2001 The transcription factor Pax6 is required for development of the diencephalic dorsal midline secretory radial glia that form the subcommissural organ. Mech Dev 109:215–224 - PubMed
-
- Gehring WJ 2005 New perspectives on eye development and the evolution of eyes and photoreceptors. J Hered 96:171–184 - PubMed
-
- Walther C, Gruss P 1991 Pax-6, a murine paired box gene, is expressed in the developing CNS. Development 113:1435–1449 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

