ATP release from the human ureter on distension and P2X(3) receptor expression on suburothelial sensory nerves
- PMID: 18819020
- PMCID: PMC2583211
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-008-9123-1
ATP release from the human ureter on distension and P2X(3) receptor expression on suburothelial sensory nerves
Abstract
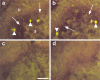
It is not clear how the increase in intraluminal pressure behind an obstructing ureteric calculus causes an increase in action potential frequency in ureteric sensory nerves so the pain messages are transmitted to the brain. It has been proposed that ureteric distension causes urothelial release of ATP, which activates purinoceptors on suburothelial nociceptive sensory nerves. The purpose of this study was to determine whether distension of the human ureter results in the release of ATP and whether the nociceptive P2 receptor, P2X(3), is expressed on suburothelial sensory nerves in the human ureter. Human ureter segments were perfused with Krebs solution and intermittently distended to a range of pressures. Samples of perfusate were collected throughout and the ATP concentration ([ATP]) was determined using a luciferin-luciferase assay. Sections of ureter were stained using antibodies against P2X(3) and capsaicin receptors (TRPV1). [ATP] rose to more than 10 times baseline levels after distension beyond a threshold of 25-30 cmH(2)O. Immunofluorescence studies on consecutive frozen sections showed that suburothelial nerves stained positively for P2X(3) and capsaicin receptors, with no staining in controls. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that purinergic signalling is involved in human ureteric mechanosensory transduction, leading to nociception.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ATP is released from guinea pig ureter epithelium on distension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002 Feb;282(2):F281-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00293.2000. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11788442
-
Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Jun;110(3):433-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.013. Epub 2005 Oct 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16226312 Review.
-
Alterations in P2X and P2Y purinergic receptor expression in urinary bladder from normal cats and cats with interstitial cystitis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004 Nov;287(5):F1084-91. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00118.2004. Epub 2004 Jul 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15251862
-
Purinergic signalling in the lower urinary tract.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013 Jan;207(1):40-52. doi: 10.1111/apha.12012. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013. PMID: 23176070 Review.
-
Purinergic component of mechanosensory transduction is increased in a rat model of colitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Sep;287(3):G647-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00020.2004. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15331354
Cited by
-
Introduction and perspective, historical note.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 21;7:227. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00227. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24312014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic mechanosensory transduction and visceral pain.Mol Pain. 2009 Nov 30;5:69. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-69. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19948030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic signalling in the urinary tract in health and disease.Purinergic Signal. 2014 Mar;10(1):103-55. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9395-y. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Purinergic Signal. 2014. PMID: 24265069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the urothelium intelligent?Neurourol Urodyn. 2010 Apr;29(4):598-602. doi: 10.1002/nau.20914. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010. PMID: 20432319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for ATP in bronchoconstriction-induced activation of guinea pig vagal intrapulmonary C-fibres.J Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;590(16):4109-20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.233460. Epub 2012 Jun 11. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22687618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '13137835', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13137835/'}]}
- Risholm L (1954) Studies on renal colic and its treatment by posterior splanchnic block. Acta Chir Scand Suppl 184:5–64 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1191907', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1191907/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2466985', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2466985/'}]}
- Amann R, Dray A, Hankins MW (1988) Stimulation of afferent fibres of the guinea-pig ureter evokes potentials in inferior mesenteric ganglion neurones. J Physiol 402:543–553 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0165-1838(94)90053-1', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1838(94)90053-1'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7525686', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7525686/'}]}
- Edyvane KA, Smet PJ, Trussell DC et al (1994) Patterns of neuronal colocalisation of tyrosine hydroxylase, neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in human ureter. J Auton Nerv Syst 48:241–255. doi:10.1016/0165-1838(94)90053-1 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9535931', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9535931/'}]}
- Roza C, Laird JM, Cervero F (1998) Spinal mechanisms underlying persistent pain and referred hyperalgesia in rats with an experimental ureteric stone. J Neurophysiol 79:1603–1612 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0006-8993(89)91058-5', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)91058-5'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2804625', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2804625/'}]}
- Ammons WS (1989) Primate spinothalamic cell responses to ureteral occlusion. Brain Res 496:124–130. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(89)91058-5 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

