FOXP3 expression accurately defines the population of intratumoral regulatory T cells that selectively accumulate in metastatic melanoma lesions
- PMID: 18820132
- PMCID: PMC2954707
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-163048
FOXP3 expression accurately defines the population of intratumoral regulatory T cells that selectively accumulate in metastatic melanoma lesions
Abstract
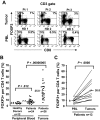
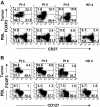
Regulatory T (T(reg)) cells are often found in human tumors; however, their functional characteristics have been difficult to evaluate due to low cell numbers and the inability to adequately distinguish between activated and T(reg) cell populations. Using a novel approach, we examined the intracellular cytokine production capacity of tumor-infiltrating T cells in the single-cell suspensions of enzymatically digested tumors to differentiate T(reg) cells from effector T cells. Similar to T(reg) cells in the peripheral blood of healthy individuals, tumor-infiltrating FOXP3(+)CD4 T cells, unlike FOXP3(-) T cells, were unable to produce IL-2 and IFN-gamma upon ex vivo stimulation, indicating that FOXP3 expression is a valid biological marker for human T(reg) cells even in the tumor microenvironment. Accordingly, we enumerated FOXP3(+)CD4 T(reg) cells in intratumoral and peritumoral sections of metastatic melanoma tumors and found a significant increase in proportion of FOXP3(+)CD4 T(reg) cells in the intratumoral compared with peritumoral areas. Moreover, their frequencies were 3- to 5-fold higher in tumors than in peripheral blood from the same patients or healthy donors, respectively. These findings demonstrate that the tumor-infiltrating CD4 T(reg) cell population is accurately depicted by FOXP3 expression, they selectively accumulate in tumors, and their frequency in peripheral blood does not properly reflect tumor microenvironment.
Figures
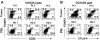


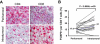
References
-
- Baecher-Allan C, Viglietta V, Hafler DA. Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–1061. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Rudensky AY. A well adapted regulatory contrivance: regulatory T cell development and the forkhead family transcription factor Foxp3. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler SF. FOXP3: of mice and men. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:209–226. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

