Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a proximal mediator of synergistic hepatotoxicity from trovafloxacin/lipopolysaccharide coexposure
- PMID: 18820134
- PMCID: PMC2685899
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.143792
Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a proximal mediator of synergistic hepatotoxicity from trovafloxacin/lipopolysaccharide coexposure
Abstract
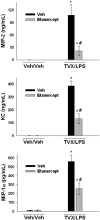
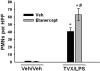
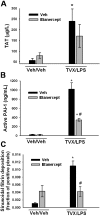
The use of trovafloxacin (TVX), a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, was severely restricted because of an association of TVX therapy with idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity in patients. The mechanisms underlying idiosyncratic toxicity are unknown; however, one hypothesis is that an inflammatory stress can render an individual sensitive to the drug. Previously, we reported that treatment of mice with TVX and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha-dependent liver injury, whereas TVX or LPS treatment alone was nontoxic. The goal of this study was to elucidate the role of TNFalpha in TVX/LPS-induced liver injury. TNF receptor (TNFR) 1 p55(-/-) and TNFR2 (p75(-/-)) mice were protected from hepatotoxicity caused by TVX/LPS coexposure, suggesting that TVX/LPS-induced liver injury requires both TNF receptors. TNFalpha inhibition using etanercept significantly reduced the TVX/LPS-induced increases in the plasma concentrations of several cytokines around the time of onset of liver injury. However, despite the reduction in chemokines, etanercept treatment did not affect the TVX/LPS-induced hepatic accumulation of neutrophils. In addition, etanercept treatment attenuated TVX/LPS induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and this was associated with a reduction in hepatic fibrin deposition. Mice treated with TVX and a nontoxic dose of TNFalpha also developed liver injury. In summary, TNFalpha acts through p55 and p75 receptors to precipitate an innocuous inflammatory cascade. TVX enhances this cascade, converting it into one that results in hepatocellular injury.
Figures


References
-
- Bertino J Jr and Fish D (2000) The safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Clin Ther 22 798-817; discussion 797. - PubMed
-
- Chen HJ, Bloch KJ, and Maclean JA (2000) Acute eosinophilic hepatitis from trovafloxacin. N Engl J Med 342 359-360. - PubMed
-
- Copple BL, Banes A, Ganey PE, and Roth RA (2002) Endothelial cell injury and fibrin deposition in rat liver after monocrotaline exposure. Toxicol Sci 65 309-318. - PubMed
-
- Dopp JM, Sarafian TA, Spinella FM, Kahn MA, Shau H, and de Vellis J (2002) Expression of the p75 TNF receptor is linked to TNF-induced NFkappaB translocation and oxyradical neutralization in glial cells. Neurochem Res 27 1535-1542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

