Ensemble modeling of metabolic networks
- PMID: 18820235
- PMCID: PMC2599852
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.108.135442
Ensemble modeling of metabolic networks
Abstract
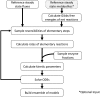
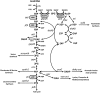
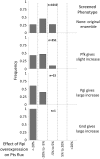
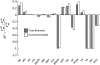
Complete modeling of metabolic networks is desirable, but it is difficult to accomplish because of the lack of kinetics. As a step toward this goal, we have developed an approach to build an ensemble of dynamic models that reach the same steady state. The models in the ensemble are based on the same mechanistic framework at the elementary reaction level, including known regulations, and span the space of all kinetics allowable by thermodynamics. This ensemble allows for the examination of possible phenotypes of the network upon perturbations, such as changes in enzyme expression levels. The size of the ensemble is reduced by acquiring data for such perturbation phenotypes. If the mechanistic framework is approximately accurate, the ensemble converges to a smaller set of models and becomes more predictive. This approach bypasses the need for detailed characterization of kinetic parameters and arrives at a set of models that describes relevant phenotypes upon enzyme perturbations.
Figures






References
-
- Lee, D. Y., C. Yun, A. Cho, B. K. Hou, S. Park, and S. Y. Lee. 2006. WebCell: a web-based environment for kinetic modeling and dynamic simulation of cellular networks. Bioinformatics. 22:1150–1151. - PubMed
-
- Segrè, D., J. Zucker, J. Katz, X. Lin, P. D'Haeseleer, W. P. Rindone, P. Kharchenko, D. H. Nguyen, M. A. Wright, and G. M. Church. 2003. From annotated genomes to metabolic flux models and kinetic parameter fitting. OMICS. 7:301–316. - PubMed
-
- Chassagnole, C., N. Noisommit-Rizzi, J. W. Schmid, K. Mauch, and M. Reuss. 2002. Dynamic modeling of the central carbon metabolism of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 79:53–73. - PubMed
-
- Savageau, M. A. 1969. Biochemical systems analysis. I. Some mathematical properties of the rate law for the component enzyme reactions. J. Theor. Biol. 25:365–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

