Molecular regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons of cerebral cortex
- PMID: 18820287
- PMCID: PMC2677647
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhn167
Molecular regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons of cerebral cortex
Abstract
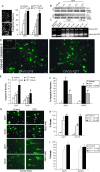
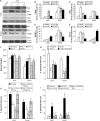
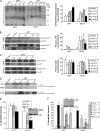
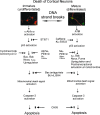
Cerebral cortical neuron degeneration occurs in brain disorders manifesting throughout life, but the mechanisms are understood poorly. We used cultured embryonic mouse cortical neurons and an in vivo mouse model to study mechanisms of DNA damaged-induced apoptosis in immature and differentiated neurons. p53 drives apoptosis of immature and differentiated cortical neurons through its rapid and prominent activation stimulated by DNA strand breaks induced by topoisomerase-I and -II inhibition. Blocking p53-DNA transactivation with alpha-pifithrin protects immature neurons; blocking p53-mitochondrial functions with mu-pifithrin protects differentiated neurons. Mitochondrial death proteins are upregulated in apoptotic immature and differentiated neurons and have nonredundant proapoptotic functions; Bak is more dominant than Bax in differentiated neurons. p53 phosphorylation is mediated by ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase. ATM inactivation is antiapoptotic, particularly in differentiated neurons, whereas inhibition of c-Abl protects immature neurons but not differentiated neurons. Cell death protein expression patterns in mouse forebrain are mostly similar to cultured neurons. DNA damage induces prominent p53 activation and apoptosis in cerebral cortex in vivo. Thus, DNA strand breaks in cortical neurons induce rapid p53-mediated apoptosis through actions of upstream ATM and c-Abl kinases and downstream mitochondrial death proteins. This molecular network operates through variations depending on neuron maturity.
Figures



References
-
- Adamec E, Vonsattel JP, Nixon RA. DNA strand breaks in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1999;849:67–77. - PubMed
-
- Bendixen C, Thomsen B, Alsner J, Westergaard O. Camptothecin-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA adducts cause premature termination of transcription. Biochemistry. 1990;29:5613–5619. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi P, Krauskopf A, Basso E, Petronilli V, Blalchy-Dyson E, Di Lisa F, Forte MA. The mitochondrial permeability transition from in vitro artifact to disease target. FEBS J. 2006;273:2077–2099. - PubMed
-
- Blasina A, Price BD, Turenne GA, McGowan CH. Caffeine inhibits the checkpoint kinase ATM. Curr Biol. 1999;9:1135–1138. - PubMed
-
- Bombrun A, Gerber P, Casi G, Terradillos O, Antonsson B, Halazy S. 3,6-Dibromocarbazole piperazine derivatives of 2-propanol as first inhibitors of cytochrome c release via bax channel modulation. J Med Chem. 2003;46:4365–4368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

