Mitochondrial tRNAThr G15927A mutation may modulate the phenotypic manifestation of ototoxic 12S rRNA A1555G mutation in four Chinese families
- PMID: 18820594
- PMCID: PMC2905378
- DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283131661
Mitochondrial tRNAThr G15927A mutation may modulate the phenotypic manifestation of ototoxic 12S rRNA A1555G mutation in four Chinese families
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the role of mitochondrial modifiers in the development of deafness associated with 12S rRNA A1555G mutation.
Methods: Four Chinese families with nonsyndromic and aminoglycoside-induced deafness were studied by clinical and genetic evaluation, molecular and biochemical analyses of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
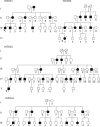
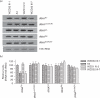
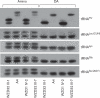
Results: These families exhibited high penetrance and expressivity of hearing impairment. Penetrances of hearing loss in WZD31, WZD32, WZD33, and WZD34 pedigrees ranged from 50 to 67% and from 39 to 50%, respectively, when aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss was included or excluded. Matrilineal relatives in these families developed hearing loss at the average of 14, 13, 16, and 15 years of age, respectively, when aminoglycoside-induced deafness was excluded. Mutational analysis of entire mtDNA in these families showed the homoplasmic A1555G mutation and distinct sets of variants belonging to haplogroup B5b1. Of these, the tRNA G15927A mutation locates at the fourth base in the anticodon stem (conventional position 42) of tRNA. A guanine (G42) at this position of tRNA is highly conserved from bacteria to human mitochondria. The lower levels and altered electrophoretic mobility of tRNA were observed in cells carrying A1555G and G15927A mutations or only G15927A mutation but not cells carrying only A1555G mutation. The abolished base pairing (28C-42G) of this tRNA by the G15927A mutation caused a failure in tRNA metabolism, worsening the mitochondrial dysfunctions altered by the A1555G mutation.
Conclusion: The G15927A mutation has a potential modifier role in increasing the penetrance and expressivity of the deafness-associated 12S rRNA A1555G mutation in those Chinese pedigrees.
Figures
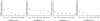

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial ND5 T12338C, tRNA(Cys) T5802C, and tRNA(Thr) G15927A variants may have a modifying role in the phenotypic manifestation of deafness-associated 12S rRNA A1555G mutation in three Han Chinese pedigrees.Am J Med Genet A. 2008 May 15;146A(10):1248-58. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32285. Am J Med Genet A. 2008. PMID: 18386806
-
Mitochondrial tRNA(Glu) A14693G variant may modulate the phenotypic manifestation of deafness-associated 12S rRNA A1555G mutation in a Han Chinese family.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Apr;36(4):241-50. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60111-3. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19376484
-
[Mitochondrial tRNAThr G15927A mutation may influence the phenotypic manifestation of deafness-associated 12S rRNA A1555G mutation.].Yi Chuan. 2008 Oct;30(10):1287-94. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2008.01287. Yi Chuan. 2008. PMID: 18930888 Chinese.
-
[Modifier factors influencing the phenotypic manifestation of the deafness associated mitochondrial DNA mutations].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;28(2):165-71. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2011.02.010. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21462128 Review. Chinese.
-
The role of mitochondrial DNA mutations in hearing loss.Biochem Genet. 2013 Aug;51(7-8):588-602. doi: 10.1007/s10528-013-9589-6. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Biochem Genet. 2013. PMID: 23605717 Review.
Cited by
-
Human mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase corrects mitochondrial dysfunctions due to the tRNALeu(UUR) A3243G mutation, associated with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like symptoms and diabetes.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 May;30(9):2147-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01614-09. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20194621 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational Analysis of Mitochondrial tRNA Genes in 200 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Sep 16;14:5719-5735. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S330973. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34557026 Free PMC article.
-
A hypertension-associated mitochondrial DNA mutation introduces an m1G37 modification into tRNAMet, altering its structure and function.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 26;293(4):1425-1438. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000317. Epub 2017 Dec 8. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29222331 Free PMC article.
-
PharmGKB summary: very important pharmacogene information for MT-RNR1.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2016 Dec;26(12):558-567. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000247. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27654872 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Contribution of the tRNAIle 4317A→G mutation to the phenotypic manifestation of the deafness-associated mitochondrial 12S rRNA 1555A→G mutation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 2;293(9):3321-3334. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000530. Epub 2018 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29348176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischel-Ghodsian N. Genetic factors in aminoglycoside toxicity. Pharmacogenomics. 2005;6:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Guan MX. Prevalence of mitochondrial 12S rRNA mutations associated with aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Voltra Rev. 2005;105:211–237. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Ballesteros M, Olarte M, Aguirre LA, Galan F, Galan R, Vallejo LA, et al. Molecular and clinical characterisation of three Spanish families with maternally inherited non-syndromic hearing loss caused by the 1494C- > T mutation in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene. J Med Genet. 2006;43:e54. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

