Central muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in pilocarpine-induced salivation, hypertension and water intake
- PMID: 18820713
- PMCID: PMC2607201
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.355
Central muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in pilocarpine-induced salivation, hypertension and water intake
Abstract
Background and purpose: Recent evidence has suggested that pilocarpine (ACh receptor agonist) injected peripherally may act centrally producing salivation and hypertension. In this study, we investigated the effects of specific M(1) (pirenzepine), M(2)/M(4) (methoctramine), M(1)/M(3) (4-DAMP) and M(4) (tropicamide) muscarinic receptor subtype antagonists injected into the lateral cerebral ventricle (LV) on salivation, water intake and pressor responses to peripheral pilocarpine.
Experimental approach: Male Holtzman rats with stainless steel cannulae implanted in the LV were used. Salivation was measured in rats anaesthetized with ketamine (100 mg per kg body weight) and arterial pressure was recorded in unanaesthetized rats.
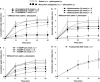
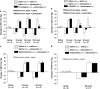
Key results: Salivation induced by i.p. pilocarpine (4 micromol per kg body weight) was reduced only by 4-DAMP (25-250 nmol) injected into the LV, not by pirenzepine, methoctramine or tropicamide at the dose of 500 nmol. Pirenzepine (0.1 and 1 nmol) and 4-DAMP (5 and 10 nmol) injected into the LV reduced i.p. pilocarpine-induced water intake, whereas metoctramine (50 nmol) produced nonspecific effects on ingestive behaviours. Injection of pirenzepine (100 nmol) or 4-DAMP (25 and 50 nmol) into the LV reduced i.v. pilocarpine-induced pressor responses. Tropicamide (500 nmol) injected into the LV had no effect on pilocarpine-induced salivation, pressor responses or water intake.
Conclusions and implications: The results suggest that central M(3) receptors are involved in peripheral pilocarpine-induced salivation and M(1) receptors in water intake and pressor responses. The involvement of M(3) receptors in water intake and pressor responses is not clear because 4-DAMP blocks both M(1) and M(3) receptors.
Figures
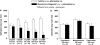
Similar articles
-
Role of the medial septal area on pilocarpine-induced salivary secretion and water intake.Brain Res. 2009 Nov 17;1298:145-52. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.067. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19728997
-
Central muscarinic and LPBN mechanisms on sodium intake.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Jan;144:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30391542
-
Central muscarinic receptors signal pilocarpine-induced salivation.J Dent Res. 2003 Dec;82(12):993-7. doi: 10.1177/154405910308201211. J Dent Res. 2003. PMID: 14630901
-
Studies of muscarinic receptor subtypes in salivary gland function in anaesthetized rats.Auton Neurosci. 2002 Sep 30;100(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s1566-0702(02)00139-x. Auton Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12422954
-
Brain muscarinic receptor subtypes mediating water intake and Fos following cerebroventricular administration of bethanecol in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 May;167(2):174-9. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1394-1. Epub 2003 Mar 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12655462
Cited by
-
Salivary gland function, development, and regeneration.Physiol Rev. 2022 Jul 1;102(3):1495-1552. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2021. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35343828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel choline analog 2-(4-((1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethan-1-ol produces sympathoinhibition, hypotension, and antihypertensive effects.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;392(9):1071-1083. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01649-8. Epub 2019 May 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31049606
-
The acetylcholine signaling network of corneal epithelium and its role in regulation of random and directional migration of corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 30;55(10):6921-33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14667. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25270189 Free PMC article.
-
Thirst sensation and oral dryness following alcohol intake.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2017 Aug;53(3):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2017. PMID: 28725298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilocarpine induces the residual secretion of salivary fluid in perfused submandibular glands of rats.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 28;14(8):e0221832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221832. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31461497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslan N, Goren Z, Onat F, Oktay S. Carbachol-induced pressor responses and muscarinic M1 receptors in the central nucleus of amydala in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997;333:63–67. - PubMed
-
- Brann MR, Ellis J, Jorgensen H, Hill-Eubanks D, Jones SV. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes: localization and structure/function. Prog Brain Res. 1993;98:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Compton J, Martinez JR, Martinez AM, Young JA. Fluid and electrolyte secretion from the isolated, perfused submandibular and sublingual glands of the rat. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26:555–561. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson MM. Pilocarpine and other cholinergic drugs in the management of salivary gland dysfunction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993;75:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Fisher AE, Coury JN. Chemical tracing of a central neural circuit underlying the thirst drive. Science. 1962;138:691–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

