Proximal humerus reconstructions for tumors
- PMID: 18820983
- PMCID: PMC2650043
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0531-x
Proximal humerus reconstructions for tumors
Abstract
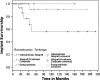
The optimal method for reconstructing the proximal humerus in patients with tumors is controversial. To determine functional outcomes and complication rates after different types of reconstructions, we reviewed a consecutive series of 49 patients who underwent proximal humerus resection and osteoarticular allograft (17 patients), allograft-prosthetic composite (16), or endoprosthetic (16) reconstruction. Operative indications included primary malignancies (24 patients), metastatic disease (19), and benign aggressive disease (six). Implant revision was more common after osteoarticular reconstruction (five of 17) than after allograft-prosthetic composite (one of 16) or endoprosthetic (zero of 16) reconstructions. At a minimum followup of 24 months (median, 98 months; range, 24-214 months) in surviving patients, Musculoskeletal Tumor Society functional scores averaged 79% for the allograft-prosthetic composite, 71% for the osteoarticular allograft, and 69% for the endoprosthetic reconstruction cohorts. Shoulder instability was associated with abductor mechanism compromise and was more common after endoprosthetic reconstruction. Allograft fractures occurred in 53% of patients receiving osteoarticular allografts. We recommend allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction for younger patients with primary tumors of bone and endoprosthetic reconstruction for older patients with metastatic disease. Because of the unacceptable complication rate, we do not recommend osteoarticular allograft reconstruction for routine use in the proximal humerus.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00003086-199903000-00025', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199903000-00025'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10101327', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10101327/'}]}
- Asavamongkolkul A, Eckardt JJ, Eilber FR, Dorey FJ, Ward WG, Kelly CM, Wirganowicz PZ, Kabo JM. Endoprosthetic reconstruction for malignant upper extremity tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;360:207–220. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/01.blo.0000093848.72468.cb', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000093848.72468.cb'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14600610', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14600610/'}]}
- Bell RS. Treatment of axial skeleton bone metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;415(suppl):S198–S200. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.jse.2006.12.006', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2006.12.006'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17560808', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17560808/'}]}
- Black AW, Szabo RM, Titelman RM. Treatment of malignant tumors of the proximal humerus with allograft-prosthesis composite reconstruction. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:525–533. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3665239', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3665239/'}]}
- Bos G, Sim F, Pritchard D, Shives T, Rock M, Askew L, Chao E. Prosthetic replacement of the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;224:178–191. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1302/0301-620X.84B8.13508', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.84b8.13508'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12463662', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12463662/'}]}
- Chen WM, Chen TH, Huang CK, Chiang CC, Lo WH. Treatment of malignant bone tumours by extracorporeally irradiated autograft-prosthetic composite arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:1156–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

