Junctional adhesion molecule C mediates leukocyte adhesion to rheumatoid arthritis synovium
- PMID: 18821692
- PMCID: PMC2911024
- DOI: 10.1002/art.23867
Junctional adhesion molecule C mediates leukocyte adhesion to rheumatoid arthritis synovium
Abstract
Objective: Leukocyte infiltration into the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium is a multistep process in which leukocytes leave the bloodstream and invade the synovial tissue (ST). Leukocyte transendothelial migration and adhesion to RA ST requires adhesion molecules on the surface of endothelial cells and RA ST fibroblasts. This study was undertaken to investigate the role of junctional adhesion molecule C (JAM-C) in mediating leukocyte recruitment and retention in the RA joint.
Methods: Immunohistologic analysis was performed on RA, osteoarthritis (OA), and normal ST samples to quantify JAM-C expression. Fibroblast JAM-C expression was also analyzed using Western blotting, cell surface enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunofluorescence. To determine the role of JAM-C in leukocyte retention in the RA synovium, in vitro and in situ adhesion assays and RA ST fibroblast transmigration assays were performed.
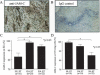
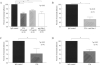
Results: JAM-C was highly expressed by RA ST lining cells, and its expression was increased in OA ST and RA ST endothelial cells compared with normal ST endothelial cells. JAM-C was also expressed on the surface of OA ST and RA ST fibroblasts. Furthermore, we demonstrated that myeloid U937 cell adhesion to both OA ST and RA ST fibroblasts and to RA ST was dependent on JAM-C. U937 cell migration through an RA ST fibroblast monolayer was enhanced in the presence of neutralizing antibodies against JAM-C.
Conclusion: Our results highlight the novel role of JAM-C in recruiting and retaining leukocytes in the RA synovium and suggest that targeting JAM-C may be important in combating inflammatory diseases such as RA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression and function of junctional adhesion molecule-C in human and experimental arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R65. doi: 10.1186/ar2223. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17612407 Free PMC article.
-
Fucosyltransferase 1 mediates angiogenesis, cell adhesion and rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue fibroblast proliferation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Jan 28;16(1):R28. doi: 10.1186/ar4456. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24467809 Free PMC article.
-
Immunolocalization of endothelial and leukocyte adhesion molecules in human rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovial tissues.Lab Invest. 1991 Mar;64(3):313-20. Lab Invest. 1991. PMID: 1706003
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
-
Junctional adhesion molecule-C: A multifunctional mediator of cell adhesion.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 13;82(1):312. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05829-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40801950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Lnc-ENST00000602558/IGF1 axis as a predictor of response to treatment with tripterygium glycosides in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jan;12(1):e1098. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1098. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38270302 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade but not overexpression of the junctional adhesion molecule C influences virus-induced type 1 diabetes in mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054675. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372751 Free PMC article.
-
Downstream gene activation of the receptor ALX by the agonist annexin A1.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 17;5(9):e12771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012771. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20862244 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell Junctional Adhesion Molecules: Role and Regulation of Expression in Inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Oct;36(10):2048-2057. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307610. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27515379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis.Angiogenesis. 2015 Oct;18(4):433-48. doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9477-2. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Angiogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26198292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Szekanecz Z, Szegedi G, Koch AE. Cellular adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by cytokines and possible clinical importance. J Investig Med. 1996;44:124–35. - PubMed
-
- Johnson BA, Haines GK, Harlow LA, Koch AE. Adhesion molecule expression in human synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36:137–46. - PubMed
-
- Van Dinther-Janssen AC, Kraal G, van Soesbergen RM, Scheper RJ, Meijer CJ. Immunohistological and functional analysis of adhesion molecule expression in the rheumatoid synovial lining layer: implications for synovial lining cell destruction. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:1998–2004. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham SA, Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Bjercke RJ, Vander-slice P, Morris AP, et al. A novel protein with homology to the junctional adhesion molecule: characterization of leukocyte interactions. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34750–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

