The Cues and Care Trial: a randomized controlled trial of an intervention to reduce maternal anxiety and improve developmental outcomes in very low birthweight infants
- PMID: 18822128
- PMCID: PMC2572053
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-8-38
The Cues and Care Trial: a randomized controlled trial of an intervention to reduce maternal anxiety and improve developmental outcomes in very low birthweight infants
Abstract
Background: Very low birthweight infants are at risk for deficits in cognitive and language development, as well as attention and behaviour problems. Maternal sensitive behaviour (i.e. awareness of infant cues and appropriate responsiveness to those cues) in interaction with her very low birthweight infant is associated with better outcomes in these domains; however, maternal anxiety interferes with the mother's ability to interact sensitively with her very low birthweight infant. There is a need for brief, cost-effective and timely interventions that address both maternal psychological distress and interactive behaviour. The Cues and Care trial is a randomized controlled trial of an intervention designed to reduce maternal anxiety and promote sensitive interaction in mothers of very low birthweight infants.
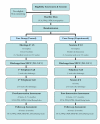
Methods and design: Mothers of singleton infants born at weights below 1500 g are recruited in the neonatal intensive care units of 2 tertiary care hospitals, and are randomly assigned to the experimental (Cues) intervention or to an attention control (Care) condition. The Cues intervention teaches mothers to attend to their own physiological, cognitive, and emotional cues that signal anxiety and worry, and to use cognitive-behavioural strategies to reduce distress. Mothers are also taught to understand infant cues and to respond sensitively to those cues. Mothers in the Care group receive general information about infant care. Both groups have 6 contacts with a trained intervener; 5 of the 6 sessions take place during the infant's hospitalization, and the sixth contact occurs after discharge, in the participant mother's home. The primary outcome is maternal symptoms of anxiety, assessed via self-report questionnaire immediately post-intervention. Secondary outcomes include maternal sensitive behaviour, maternal symptoms of posttraumatic stress, and infant development at 6 months corrected age.
Discussion: The Cues and Care trial will provide important information on the efficacy of a brief, skills-based intervention to reduce anxiety and increase sensitivity in mothers of very low birthweight infants. A brief intervention of this nature may be more readily implemented as part of standard neonatal intensive care than broad-based, multi-component interventions. By intervening early, we aim to optimize developmental outcomes in these high risk infants.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN00918472. The Cues and Care Trial: A randomized controlled trial of an intervention to reduce maternal anxiety and improve developmental outcomes in very low birthweight infants.
Figures
References
-
- Gray RF, Indurkhya A, McCormick MC. Prevalence, stability, and predictors of clinically significant behavior problems in low birth weight children at 3, 5, and 8 years of age. Pediatrics. 2004;114:736–743. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta AT, Cleves MA, Casey PH, Cradock MM, Anand KJS. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: A meta-analysis. JAMA. 2002;288:728–737. - PubMed
-
- Breslau N, Chilcoat H. Psychiatric sequelae of low birth weight at 11 years. Biological Psychiatry. 2000;47:1005–1011. - PubMed
-
- Hille ETM, den Ouden AL, Saigal S, Wolke D, Lambert M, Whitaker A, et al. Behavioral problems in children who weigh 1000 grams or less at birth in four countries. The Lancet. 2001;357:1641–1643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical