Neuraminidase activity provides a practical read-out for a high throughput influenza antiviral screening assay
- PMID: 18822145
- PMCID: PMC2562994
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-109
Neuraminidase activity provides a practical read-out for a high throughput influenza antiviral screening assay
Abstract
Background: The emergence of influenza strains that are resistant to commonly used antivirals has highlighted the need to develop new compounds that target viral gene products or host mechanisms that are essential for effective virus replication. Existing assays to identify potential antiviral compounds often use high throughput screening assays that target specific viral replication steps. To broaden the search for antivirals, cell-based replication assays can be performed, but these are often labor intensive and have limited throughput.
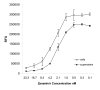
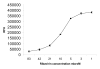
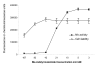
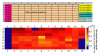
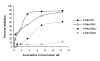
Results: We have adapted a traditional virus neutralization assay to develop a practical, cell-based, high throughput screening assay. This assay uses viral neuraminidase (NA) as a read-out to quantify influenza replication, thereby offering an assay that is both rapid and sensitive. In addition to identification of inhibitors that target either viral or host factors, the assay allows simultaneous evaluation of drug toxicity. Antiviral activity was demonstrated for a number of known influenza inhibitors including amantadine that targets the M2 ion channel, zanamivir that targets NA, ribavirin that targets IMP dehydrogenase, and bis-indolyl maleimide that targets protein kinase A/C. Amantadine-resistant strains were identified by comparing IC50 with that of the wild-type virus.
Conclusion: Antivirals with specificity for a broad range of targets are easily identified in an accelerated viral inhibition assay that uses NA as a read-out of replication. This assay is suitable for high throughput screening to identify potential antivirals or can be used to identify drug-resistant influenza strains.
Figures


References
-
- Arden NH, Patriarca PA, Kendal AP. Options for the control of influenza. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York; 1986. Experiences in the use and efficacy of inactivated influenza vaccine in nursing homes; pp. 155–168.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

