Electrostatics in the ribosomal tunnel modulate chain elongation rates
- PMID: 18822297
- PMCID: PMC2655213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.089
Electrostatics in the ribosomal tunnel modulate chain elongation rates
Abstract
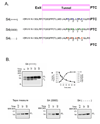
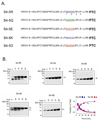
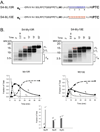
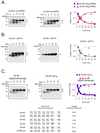
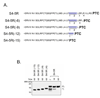
Electrostatic potentials along the ribosomal exit tunnel are nonuniform and negative. The significance of electrostatics in the tunnel remains relatively uninvestigated, yet they are likely to play a role in translation and secondary folding of nascent peptides. To probe the role of nascent peptide charges in ribosome function, we used a molecular tape measure that was engineered to contain different numbers of charged amino acids localized to known regions of the tunnel and measured chain elongation rates. Positively charged arginine or lysine sequences produce transient arrest (pausing) before the nascent peptide is fully elongated. The rate of conversion from transiently arrested to full-length nascent peptide is faster for peptides containing neutral or negatively charged residues than for those containing positively charged residues. We provide experimental evidence that extraribosomal mechanisms do not account for this charge-specific pausing. We conclude that pausing is due to charge-specific interactions between the tunnel and the nascent peptide.
Figures
References
-
- Kosolapov A, Tu L, Wang J, Deutsch C. Structure acquisition of the T1 domain of Kv1.3 during biogenesis. Neuron. 2004;44:295–307. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Deutsch C. Secondary structure formation of a transmembrane segment in Kv channels. Biochemistry. 2005;44:8230–8243. - PubMed
-
- Tu L, Wang J, Deutsch C. Biogenesis of the T1-S1 linker of voltage-gated K+ channels. Biochemistry. 2007;46:8075–8084. - PubMed
-
- Woolhead CA, McCormick PJ, Johnson AE. Nascent membrane and secretory proteins differ in FRET-detected folding far inside the ribosome and in their exposure to ribosomal proteins. Cell. 2004;116:725–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

