Pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies modulate gene expression in mesangial cells: involvement of HMGB1 in anti-DNA antibody-induced renal injury
- PMID: 18822317
- PMCID: PMC2677706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.08.007
Pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies modulate gene expression in mesangial cells: involvement of HMGB1 in anti-DNA antibody-induced renal injury
Abstract
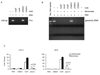
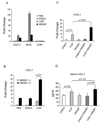
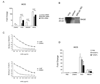
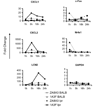
Although anti-DNA antibodies have been decisively linked to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis, the mechanisms have not been conclusively determined. Recently, we reported that anti-DNA antibodies may contribute to kidney damage by upregulation of proinflammatory genes in mesangial cells (MC), a process involving both Fc receptor-dependent and independent pathways. In investigating the mechanism by which pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies modulate gene expression in MC, we found that the pathogenic anti-DNA antibody 1A3F bound to high mobility group binding protein 1 (HMGB1), an endogenous ligand for TLR2/4 and RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products). Interestingly, HMGB1 treatment of MC induced a similar pattern of genes as stimulation with 1A3F. Furthermore, HMGB1 and 1A3F exhibited a synergistic proinflammatory effect in the kidney, where increased expression of HMGB1 was found in lupus patients but not in patients with other types of renal disease. TLR2/Fc and RAGE/Fc inhibited the proinflammatory effects of 1A3F on MC. Finally, we found enhanced susceptibility of lupus prone MRL-lpr/lpr (MRL/lpr) as compared to normal BALB/c derived MC to pathogenic anti-DNA antibody and LPS stimulation (in particular enhanced chemokine synthesis), in addition to significantly increased expression of TLR4. Our results suggest that gene upregulation in MC induced by nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies is TLR2/4 and RAGE-dependent. Finally, HMGB1 may act as a proinflammatory mediator in antibody-induced kidney damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Figures




References
-
- Foster MH, Cizman B, Madaio MP. Nephritogenic autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: immunochemical properties, mechanisms of immune deposition, and genetic origins. Lab Invest. 1993;69:494–507. - PubMed
-
- Hahn BH. Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Clynes R, Dumitru C, Ravetch JV. Uncoupling of immune complex formation and kidney damage in autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Science. 1998;279:1052–1054. - PubMed
-
- Fu Y, Xie C, Chen J, Zhu J, Zhou H, Thomas J, et al. Innate stimuli accentuate end-organ damage by nephrotoxic antibodies via Fc receptor and TLR stimulation and IL-1/TNF-alpha production. J Immunol. 2006;176:632–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

