Predictive value of MMP-7 expression for response to chemotherapy and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 18823373
- PMCID: PMC11158233
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00922.x
Predictive value of MMP-7 expression for response to chemotherapy and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
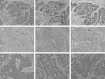
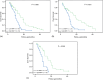
Fundamental studies have suggested that matrix metalloproteinases-7 (MMP-7) expression is associated with chemoresistance and constitutes a prognostic factor in several solid tumors. The present study assessed the prognostic and predictive value of MMP-7 in tumors of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. In total, 159 patients with stage III and IV NSCLC were retrospectively enrolled. Immunohistochemistry was performed to evaluate the expression of MMP-7, apoptosis-related proteins Bcl-2, Bax, Fas and FasL and the Ki-67 proliferation marker. The TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling) method was performed to investigate tumor apoptosis. Ninety carcinomas (56.6%) were identified as high expression of MMP-7. Overexpression of MMP-7 was more frequent in adenocarcinomas than in squamous cell carcinomas (P = 0.032). The expression of MMP-7 was positively related with Ki-67 index and Bcl-2, but not apoptosis index. MMP-7 status was correlated inversely with response to chemotherapy in overall patients (response rates, 20.0% and 35.8%, for patients with high-MMP-7 and low-MMP-7 tumors, respectively, P = 0.036), especially in adenocarcinoma (P = 0.021), but not in patients with squamous cell carcinomas (P = 0.373). The overall survival was significantly lower in NSCLC patients with high MMP-7 than in those with low MMP-7 (P < 0.001). A Cox regression analyses also demonstrated MMP-7 status to be a significant prognostic factor (hazard ratio, 5.49 P = 0.001). These findings suggest that the expression level of MMP-7 in tumor cells is predictive of response to chemotherapy and outcome in patients with advanced NSCLC receiving platinum-based chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Mantovani A, Romero P, Palucka AK, Marincola FM. Tumour immunity: effector response to tumour and role of the microenvironment. Lancet 2008; 371: 771–83. - PubMed
-
- Rintoul RC, Sethi T. Extracellular matrix regulation of drug resistance in small‐cell lung cancer. Clin Sci (Lond) 2002; 102: 417–24. - PubMed
-
- Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM et al . Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo . Nat Med 1999; 5: 662–8. - PubMed
-
- Ii M, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Maruyama Y, Shinomura Y. Role of matrix metalloproteinase‐7 (Matrilysin) in human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp Biol Med 2006; 231: 20–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

