Silence of ClC-3 chloride channel inhibits cell proliferation and the cell cycle via G/S phase arrest in rat basilar arterial smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 18823498
- PMCID: PMC6496167
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2008.00551.x
Silence of ClC-3 chloride channel inhibits cell proliferation and the cell cycle via G/S phase arrest in rat basilar arterial smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Objectives: Previously, we have found that the ClC-3 chloride channel is involved in endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced rat aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation. The present study was to investigate the role of ClC-3 in cell cycle progression/distribution and the underlying mechanisms of proliferation.
Materials and methods: Small interference RNA (siRNA) is used to silence ClC-3 expression. Cell proliferation, cell cycle distribution and protein expression were measured or detected with cell counting, bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation, Western blot and flow cytometric assays respectively.
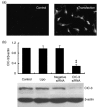
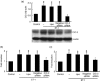
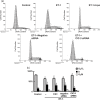
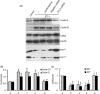
Results: ET-1-induced rat basilar vascular smooth muscle cell (BASMC) proliferation was parallel to a significant increase in endogenous expression of ClC-3 protein. Silence of ClC-3 by siRNA inhibited expression of ClC-3 protein, prevented an increase in BrdU incorporation and cell number induced by ET-1. Silence of ClC-3 also caused cell cycle arrest in G(0)/G(1) phase and prevented the cells' progression from G(1) to S phase. Knockdown of ClC-3 potently inhibited cyclin D1 and cyclin E expression and increased cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs) p27(KIP) and p21(CIP) expression. Furthermore, ClC-3 knockdown significantly attenuated phosphorylation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) induced by ET-1.
Conclusion: Silence of ClC-3 protein effectively suppressed phosphorylation of the Akt/GSK-3beta signal pathway, resulting in down-regulation of cyclin D1 and cyclin E, and up-regulation of p27(KIP) and p21(CIP). In these BASMCs, integrated effects lead to cell cycle G(1)/S arrest and inhibition of cell proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SGK1 mediates hypotonic challenge-induced proliferation in basilar artery smooth muscle cells via promoting CREB signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 May 5;898:173997. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173997. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33676941
-
ClC-2 knockdown prevents cerebrovascular remodeling via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Jun 27;23:29. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0095-z. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29988306 Free PMC article.
-
ClC-3 chloride channel modulates the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells via AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1622-30. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973047 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs) and the DNA damage response: The link between signaling pathways and cancer.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Jun;102:103103. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103103. Epub 2021 Mar 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 33812232 Review.
-
ClC-3: A Novel Promising Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Nov;26(6):550-561. doi: 10.1177/10742484211023639. Epub 2021 Jun 17. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34138674 Review.
Cited by
-
Chloride channels in stroke.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Jan;34(1):17-23. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.140. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23103617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endosomal ClC-3 and Nox1: moving marksmen of redox signaling?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Feb;31(2):240-2. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.220053. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21248280 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ano1 as a regulator of proliferation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):G1044-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00196.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21940901 Free PMC article.
-
WNK1 is required for proliferation induced by hypotonic challenge in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Jan;39(1):35-47. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.56. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 28770829 Free PMC article.
-
The chloride channel cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) controls cellular quiescence by hyperpolarizing the cell membrane during diapause in the crustacean Artemia.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 19;294(16):6598-6611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005900. Epub 2019 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30765604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barchiesi F, Jackson EK, Fingerle J, Gillespie DG, Odermatt B, Dubey RK (2006) 2‐Methoxyestradiol, an estradiol metabolite, inhibits neointima formation and smooth muscle cell growth via double blockade of the cell cycle. Circ. Res. 99, 266–274. - PubMed
-
- Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA (2004) The role of apoptotic Volume decrease and ionic homeostasis in the activation and repression of apoptosis. Pflugers Arch. 448, 313–318. - PubMed
-
- Box AH, Demetrick DJ (2004) Cell cycle kinase inhibitor expression and hypoxia‐induced cell cycle arrest in human cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis 25, 2325–2335. - PubMed
-
- Braun‐Dullaeus RC, Mann MJ, Dzau VJ (1998) Cell cycle progression: new therapeutic target for vascular proliferative disease. Circulation 98, 82–89. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Wang L, Zhu L, Nie S, Zhang J, Zhong P, Cai B, Luo H, Jacob TJ (2002) Cell cycle‐dependent expression of volume‐activated chloride currents in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 283, C1313–C1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

