Developmental hyperoxia attenuates the hypoxic ventilatory response in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica)
- PMID: 18824143
- PMCID: PMC2630527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2008.09.006
Developmental hyperoxia attenuates the hypoxic ventilatory response in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica)
Abstract
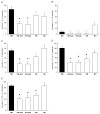
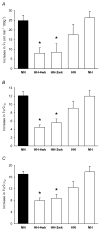
Early life experiences can influence development of the respiratory control system. We hypothesized that chronic hyperoxia (60% O(2)) during development would attenuate the hypoxic ventilatory response (HVR) of Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica), similar to the effects of developmental hyperoxia in mammals. Quail were exposed to hyperoxia during prenatal development, during postnatal development, or during both prenatal and postnatal development (for approximately 2 or 4 weeks). HVR (11% O(2)) was subsequently assessed in adults (>6 weeks old) via barometric plethysmography and compared to quail raised in normoxia (i.e., control). The HVR of quail exposed to hyperoxia both prenatally and postnatally was reduced 50-60% compared to control quail whereas postnatally exposed quail exhibited normal HVR. The effects of prenatal hyperoxia on HVR were equivocal and depended on how HVR was expressed. We conclude that developmental exposure to 60% O(2) attenuates the HVR in quail and that the critical period for this plasticity encompasses the late prenatal and early postnatal periods.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxic ventilatory response of adult rats and mice after developmental hyperoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Aug 15;177(3):342-6. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 12. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21601659 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental plasticity of the hypoxic ventilatory response after perinatal hyperoxia and hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005 Nov 15;149(1-3):287-99. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2005.04.003. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16203217 Review.
-
Chronic hyperoxia alters the early and late phases of the hypoxic ventilatory response in neonatal rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Sep;109(3):796-803. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00510.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20576840 Free PMC article.
-
Development of ventilatory chemoreflexes in Coturnix quail chicks.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020 May;276:103411. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2020.103411. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32068130
-
Effects of Perinatal Hyperoxia on Breathing.Compr Physiol. 2020 Mar 12;10(2):597-636. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190023. Compr Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32163205 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic hyperoxia and the development of the carotid body.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013 Jan 1;185(1):94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2012.05.019. Epub 2012 May 26. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 22640932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The avian embryo as a time-honoured animal model in developmental, biomedical and agricultural research.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;380(1920):20230438. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0438. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010394 Review.
-
Perinatal hyperoxic exposure reconfigures the central respiratory network contributing to intolerance to anoxia in newborn rat pups.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Jan 1;116(1):47-53. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00224.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 24157524 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic ventilatory response of adult rats and mice after developmental hyperoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Aug 15;177(3):342-6. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 12. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21601659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bavis RW, Kilgore DL., Jr Effects of embryonic CO2 exposure on the adult ventilatory response in quail: does gender matter? Respir Physiol. 2001;126:183–199. - PubMed
-
- Bavis RW, Mitchell GS. Long-term effects of the perinatal environment on respiratory control. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104:1220–1229. - PubMed
-
- Bavis RW, Olson EB, Jr, Mitchell GS. Critical developmental period for hyperoxia-induced blunting of hypoxic phrenic responses in rats. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92:1013–1018. - PubMed
-
- Bavis RW, Olson EB, Jr, Vidruk EH, Bisgard GE, Mitchell GS. Level and duration of developmental hyperoxia influence impairment of hypoxic phrenic responses in rats. J Appl Physiol. 2003;95:1550–1559. - PubMed
-
- Bavis RW, Russell KER, Simons JC, Otis JP. Hypoxic ventilatory responses in rats after hypercapnic hyperoxia and intermittent hyperoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007;155:193–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

