Hairpin structures formed by alpha satellite DNA of human centromeres are cleaved by human topoisomerase IIalpha
- PMID: 18824478
- PMCID: PMC2577340
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn640
Hairpin structures formed by alpha satellite DNA of human centromeres are cleaved by human topoisomerase IIalpha
Abstract
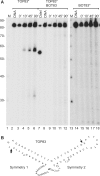
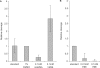
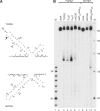
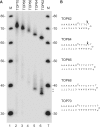
Although centromere function has been conserved through evolution, apparently no interspecies consensus DNA sequence exists. Instead, centromere DNA may be interconnected through the formation of certain DNA structures creating topological binding sites for centromeric proteins. DNA topoisomerase II is a protein, which is located at centromeres, and enzymatic topoisomerase II activity correlates with centromere activity in human cells. It is therefore possible that topoisomerase II recognizes and interacts with the alpha satellite DNA of human centromeres through an interaction with potential DNA structures formed solely at active centromeres. In the present study, human topoisomerase IIalpha-mediated cleavage at centromeric DNA sequences was examined in vitro. The investigation has revealed that the enzyme recognizes and cleaves a specific hairpin structure formed by alpha satellite DNA. The topoisomerase introduces a single-stranded break at the hairpin loop in a reaction, where DNA ligation is partly uncoupled from the cleavage reaction. A mutational analysis has revealed, which features of the hairpin are required for topoisomerease IIalpha-mediated cleavage. Based on this a model is discussed, where topoisomerase II interacts with two hairpins as a mediator of centromere cohesion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-association and DNA binding properties of the human topoisomerase IIA alpha2HTH module.Biochimie. 2006 Mar-Apr;88(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.08.003. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Biochimie. 2006. PMID: 16213649
-
Quinolone action against human topoisomerase IIalpha: stimulation of enzyme-mediated double-stranded DNA cleavage.Biochemistry. 2003 Apr 1;42(12):3393-8. doi: 10.1021/bi027383t. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12653542
-
The QTK loop is essential for the communication between the N-terminal atpase domain and the central cleavage--ligation region in human topoisomerase IIalpha.Biochemistry. 2009 Jul 14;48(27):6508-15. doi: 10.1021/bi9005978. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19485418
-
Does topoisomerase II specifically recognize and cleave hairpins, cruciforms and crossovers of DNA?Biochimie. 2007 Apr;89(4):508-15. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Feb 24. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17397986 Review.
-
[Role of nuclear matrix proteins in the formation of heterochromatin].Tsitologiia. 1999;41(7):562-73. Tsitologiia. 1999. PMID: 10496017 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of predicted DNA secondary structures infers complex human centromere topology.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Dec 5;111(12):2707-2719. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.10.016. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39561771 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of Non-B-Form DNA at D. melanogaster Centromeres.Genome Biol Evol. 2022 May 3;14(5):evac054. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evac054. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35441684 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of higher-order DNA structures by azacryptands induces DNA junction-mediated DNA damage in cancer cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Oct 11;49(18):10275-10288. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab796. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34551430 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of small molecules with DNA junctions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12636-12656. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1043. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36382400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental and chemotherapeutic agents induce breakage at genes involved in leukemia-causing gene rearrangements in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.Mutat Res. 2015 Sep;779:86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 26163765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee C, Wevrick R, Fisher RB, Ferguson-Smith MA, Lin CC. Human centromeric DNAs. Hum. Genet. 1997;100:291–304. - PubMed
-
- Choo KH. The Centromere. New York: Oxford University Press Inc; 1997.
-
- Karpen GH, Allshire RC. The case for epigenetic effects on centromere identity and function. Trends Genet. 1997;13:489–496. - PubMed
-
- Murphy TD, Karpen GH. Centromeres take flight: alpha satellite and the quest for the human centromere. Cell. 1998;93:317–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

