A novel biochemical method to identify target genes of individual microRNAs: identification of a new Caenorhabditis elegans let-7 target
- PMID: 18824511
- PMCID: PMC2578851
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1139508
A novel biochemical method to identify target genes of individual microRNAs: identification of a new Caenorhabditis elegans let-7 target
Abstract
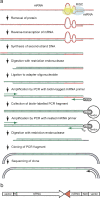
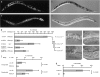
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are roughly 22-nucleotide regulatory RNAs that play important roles in many developmental and physiological processes. Animal miRNAs down-regulate target genes by forming imperfect base pairs with 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs) of their mRNAs. Thousands of miRNAs have been discovered in several organisms. However, the target genes of almost all of these miRNAs remain to be identified. Here, we describe a method for isolating cDNA clones of target mRNAs that form base pairs in vivo with an endogenous miRNA of interest, in which the cDNAs are synthesized from the mRNAs using the miRNA as a reverse-transcription primer. The application of this method to Caenorhabditis elegans miRNA lin-4 under test conditions yielded many clones of the known target gene lin-14 that correspond to partial sequences 5' to lin-4 binding sites in the 3' UTR. The method was also applied to C. elegans miRNA let-7 and a new target gene responsible for the lethal phenotype in let-7 mutants was identified. These results demonstrate that the method is a useful way to identify targets on the basis of base pairing with individual miRNAs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans period homolog lin-42 regulates the timing of heterochronic miRNA expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 28;111(43):15450-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414856111. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25319259 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation.Cell. 2005 Aug 26;122(4):553-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.031. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16122423
-
Computational analysis of microRNA targets in Caenorhabditis elegans.Gene. 2006 Jan 3;365:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.035. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16356665
-
C. elegans microRNAs.WormBook. 2005 Sep 21:1-9. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.26.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational control of endogenous microRNA target genes in C. elegans.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010;50:21-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-03103-8_2. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19841879 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1;39(16):6845-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr330. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21652644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics analysis identify novel OB fold protein coding genes in C. elegans.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 25;8(4):e62204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062204. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638006 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Argonaute RIP-Chip shows that miRNA transfections alter global patterns of mRNA recruitment to microribonucleoprotein complexes.RNA. 2010 Feb;16(2):394-404. doi: 10.1261/rna.1905910. Epub 2009 Dec 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20042474 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and identification of cell-specific microRNAs targeting a messenger RNA using a biotinylated anti-sense oligonucleotide capture affinity technique.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr 1;41(6):e71. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1466. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23325846 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in vivo precipitation identifies miR-151-3p as a computational unpredictable miRNA to target Stat3 and inhibits innate IL-6 production.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Feb;15(2):99-110. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.82. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28890541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahante J.E., Daul A.L., Li M., Volk M.L., Tennessen J.M., Miller E.A., Rougvie A.E. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev. Cell. 2003;4:625–637. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V., Lee R.C., Lavanway A., Williams P.T., Jewell D. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans . Curr. Biol. 2003;13:807–818. - PubMed
-
- Andachi Y. Caenorhabditis elegans T-box genes tbx-9 and tbx-8 are required for formation of hypodermis and body-wall muscle in embryogenesis. Genes Cells. 2004;9:331–344. - PubMed
-
- Bagga S., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
