Mechanistic diversity in the RuBisCO superfamily: a novel isomerization reaction catalyzed by the RuBisCO-like protein from Rhodospirillum rubrum
- PMID: 18826254
- PMCID: PMC2597038
- DOI: 10.1021/bi801685f
Mechanistic diversity in the RuBisCO superfamily: a novel isomerization reaction catalyzed by the RuBisCO-like protein from Rhodospirillum rubrum
Abstract
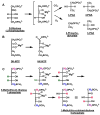
Some homologues of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) do not catalyze carboxylation and are designated RuBisCO-like proteins (RLPs). The RLP from Rhodospirillum rubrum (gi:83593333) catalyzes a novel isomerization reaction (overall 1,3-proton transfer reaction; likely, two 1,2-proton transfer reactions) that converts 5-methylthio-D-ribulose 1-phosphate to a 3:1 mixture of 1-methylthioxylulose 5-phosphate and 1-methylthioribulose 5-phosphate. Disruption of the gene encoding the RLP abolishes the ability of R. rubrum to utilize 5'-methylthioadenosine as a sole sulfur source, implicating a new, as-yet-uncharacterized, pathway for sulfur salvage.
Figures

References
-
- Cleland WW, Andrews TJ, Gutteridge S, Hartman FC, Lorimer GH. Chem Rev. 1998;98:549–562. - PubMed
-
- Larimer FW, Harpel MR, Hartman FC. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11114–20. - PubMed
-
- Morell MK, Wilkin JM, Kane HJ, Andrews TJ. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:5445–51. - PubMed
-
- Ashida H, Saito Y, Kojima C, Kobayashi K, Ogasawara N, Yokota A. Science. 2003;302:286–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

