The family check-up with high-risk indigent families: preventing problem behavior by increasing parents' positive behavior support in early childhood
- PMID: 18826532
- PMCID: PMC2683384
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01195.x
The family check-up with high-risk indigent families: preventing problem behavior by increasing parents' positive behavior support in early childhood
Abstract
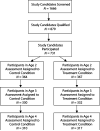
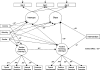
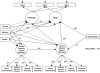
Seven hundred thirty-one income-eligible families in 3 geographical regions who were enrolled in a national food supplement program were screened and randomized to a brief family intervention. At child ages 2 and 3, the intervention group caregivers were offered the Family Check-Up and linked parenting support services. Latent growth models on caregiver reports at child ages 2, 3, and 4 revealed decreased behavior problems when compared with the control group. Intervention effects occurred predominantly among families reporting high levels of problem behavior at child age 2. Families in the intervention condition improved on direct observation measures of caregivers' positive behavior support at child ages 2 and 3; improvements in positive behavior support mediated improvements in children's early problem behavior.
Figures




References
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth & Families; Burlington: 2001. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles: Child Behavior Checklist for Ages 6−18, Teacher's Report Form, & Youth Self-Report.
-
- Baldwin DA. Understanding the link between joint attention and language. In: Dunham PJ, Moore C, editors. Joint attention: Its origins and roles in development. Erlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ: 1995. pp. 131–158.
-
- Baldwin DA, Bill B, Desjardins RN, Irwin JM, Markman EM. Infants’ reliance on social criterion for establishing word–object relations. Journal of Child Development. 1996;67:3135–3153. - PubMed
-
- Baydar N, Reid MJ, Webster-Stratton C. The role of mental health factors and program engagement in the effectiveness of a preventive parenting program for Head Start mothers. Child Development. 2003;74:1433–1453. - PubMed
-
- Bradley RH, Corwyn RF, McAdoo HP, Garcia-Coll C. The home environments of children in the United States. Part I: Variations by age, ethnicity, and poverty status. Child Development. 2001;72:1844–1867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

