Effects of school closures, 2008 winter influenza season, Hong Kong
- PMID: 18826841
- PMCID: PMC2609897
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1410.080646
Effects of school closures, 2008 winter influenza season, Hong Kong
Abstract
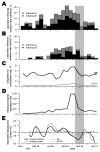
In winter 2008, kindergartens and primary schools in Hong Kong were closed for 2 weeks after media coverage indicated that 3 children had died, apparently from influenza. We examined prospective influenza surveillance data before, during, and after the closure. We did not find a substantial effect on community transmission.
Figures
Comment in
-
School closure to reduce influenza transmission.Emerg Infect Dis. 2009 Jan;15(1):137-8, author reply 138. doi: 10.3201/eid1501.081289. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19116082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
