Between-group competition and human cooperation
- PMID: 18826935
- PMCID: PMC2581672
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2008.1060
Between-group competition and human cooperation
Abstract
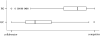
A distinctive feature of human behaviour is the widespread occurrence of cooperation among unrelated individuals. Explaining the maintenance of costly within-group cooperation is a challenge because the incentive to free ride on the efforts of other group members is expected to lead to decay of cooperation. However, the costs of cooperation can be diminished or overcome when there is competition at a higher level of organizational hierarchy. Here we show that competition between groups resolves the paradigmatic 'public goods' social dilemma and increases within-group cooperation and overall productivity. Further, group competition intensifies the moral emotions of anger and guilt associated with violations of the cooperative norm. The results suggest an important role for group conflict in the evolution of human cooperation and moral emotions.
Figures
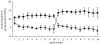

References
-
- Arrow H. The sharp end of altruism. Science. 2007;318:581–582. doi:10.1126/science.1150316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avilés L. Solving the freeloaders paradox: genetic associations and frequency-dependent selection in the evolution of cooperation among nonrelatives. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:14 268–14 273. doi:10.1073/pnas.212408299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Axelrod R., Hamilton W.D. The evolution of cooperation. Science. 1981;211:1390–1396. doi:10.1126/science.7466396 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernhard H., Fischbacher U., Fehr E. Parochial altruism in humans. Nature. 2006;442:912–915. doi:10.1038/nature04981 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bowles S. Group competition, reproductive leveling, and the evolution of human altruism. Science. 2006;314:1569–1572. doi:10.1126/science.1134829 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

