The accuracy of the Guardian RT continuous glucose monitor in children with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 18828242
- PMCID: PMC2587171
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2007.0279
The accuracy of the Guardian RT continuous glucose monitor in children with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the accuracy of the Guardian RT system (Medtronic Minimed, Northridge, CA) in young children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) during different scenarios of glucose levels and sensor age.
Methods: At five clinical centers, 30 subjects between 4 and 17 years old with T1D were recruited. All subjects had a glycosylated hemoglobin level of <or=10.0% and were using an insulin pump. Subjects initially used a Guardian RT for approximately 1 week at home. Each subject was then hospitalized overnight for about 18 h in a clinical research center, during which time insulin-induced hypoglycemia occurred, along with frequently sampled glucose.
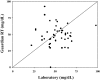
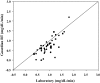
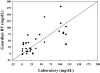
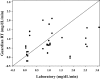
Results: There were 1,511 laboratory glucose measurements paired with glucose measurements from 48 Guardian RT sensors. Overall, the median absolute difference (AD) was 21 mg/dL, and the median relative AD (RAD) was 14%, with 64% of sensor values meeting International Organization for Standardization home glucose meter criteria. The median AD was 27 mg/dL for reference glucose values<or=60 mg/dL and 25 mg/dL for reference glucose values<or=70 mg/dL. The median RAD was 19% for reference glucose values 71-120 mg/dL, 14% for reference glucose values 121-180 mg/dL, and 10% for reference glucose values>180 mg/dL.
Conclusions: The Guardian RT appears to perform as well in children with T1D as it has been reported to perform in adults with diabetes. The Guardian RT has an accuracy similar to that of other available continuous glucose monitors and can give important and useful clinical information.
Figures
References
-
- Neese JW. Duncan P. Bayse D. Robinson M. Cooper T. Stewart C. Development, Evaluation of a Hexokinase/Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Procedure for Use as a National Glucose Reference Method. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control; 1976.
-
- Passey RB. Gillum RL. Fuller JB. Urry FM. Giles ML. Evaluation and comparison of 10 glucose methods and the reference method recommended in the proposed product class standard (1974) Clin Chem. 1977;23:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group. A multicenter study of the accuracy of the OneTouch Ultra home glucose meter in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2003;5:933–941. - PubMed
-
- International Organization for Standardization. Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: Switzerland: 2003.
-
- Efron B. Tibshirani R. An introduction to the Bootstrap. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

